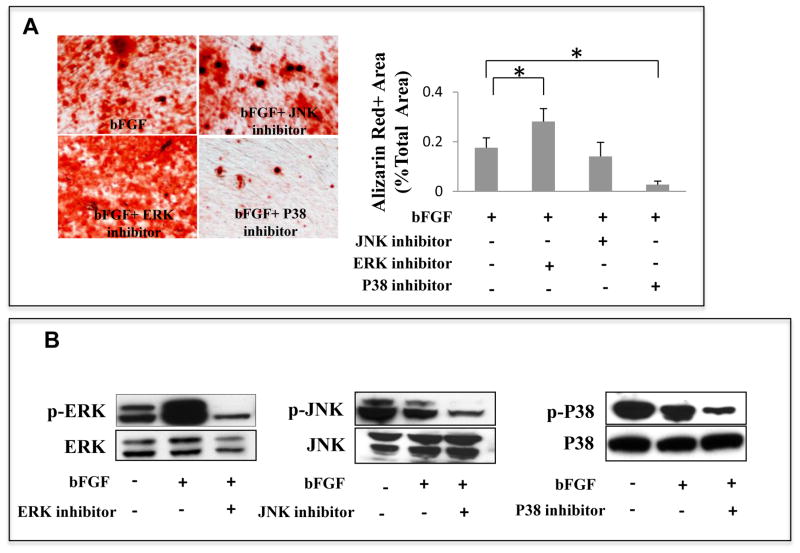
Figure 2. ERK1/2 is down stream target of bFGF-induced osteogenesis deficiency in SHED.
(A) After 4 weeks osteogenic culture induction, bFGF-treated SHED showed a reduction in mineralized nodule formation, which was rescued by the ERK1/2 inhibitor treatment as assessed by alizarin red staining. However, the JNK and P38 inhibitors did not show any restoration of bFGF-induced reduction of mineralized nodule formation in SHED. Alizarin red-positive (Alizarin Red+) area corresponding to total area was averaged from five independent groups. (B) Western blot analysis showed that bFGF treatment increased phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK) and the ERK1/2 inhibitor treatment reduced level of phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK). bFGF appeared to decrease phosphorylated JNK (pJNK) and P38 (pP38). The JNK and P38 inhibitor treatment reduced levels of phosphorylated JNK (pJNK) and P38 (p-P38).(*P<0.05).