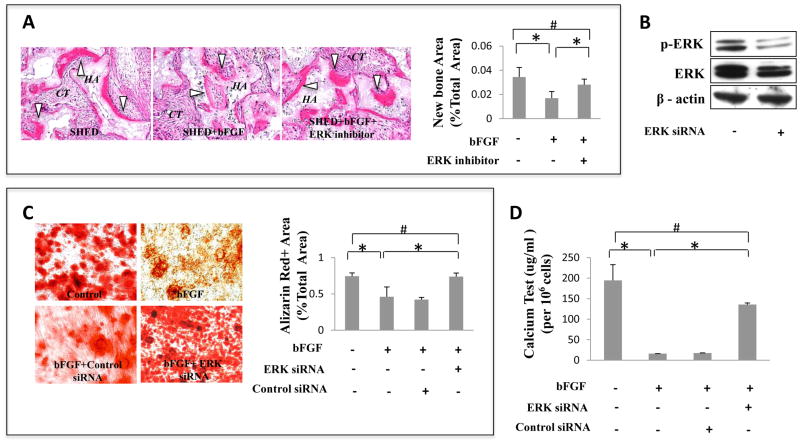
Figure 3. Blockage of ERK1/2 signaling rescued bFGF-induced osteogenic deficiency of SHED.
(A) The ERK1/2 inhibitor treatment rescued bFGF-induced reduction of SHED-mediated bone formation (B white triangle) as assessed by subcutaneously implantation into immunocompromised mice using HA/TCP (HA) as carrier. Newly formed bone area was calculated as a percentage of total area and averaged from three independent transplant assays. (B) Western blot analysis showed that ERK1/2 siRNA blocked phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK). β-actin was used as an internal control. Three independent assays showed similar results. (C) After 4 weeks culture induction in osteogenic medium, bFGF-treated SHED showed decreased mineralized nodule formation than control group as assessed by alizarin red staining. ERK1/2 siRNA rescued bFGF-induced reduction of mineralized nodule formation, but control siRNA didn’t rescue the reduction. Alizarin red-positive (Alizarin Red+) area corresponding to total area was averaged from five independent groups (*P<0.05). (D) After 4 weeks culture induction in osteogenic medium, bFGF-treated SHED showed decreased calcium level of extracellular matrix than control group. ERK1/2 siRNA rescued bFGF-induced reduction of calcium level, but control siRNA didn’t rescue the reduction (*P<0.05).