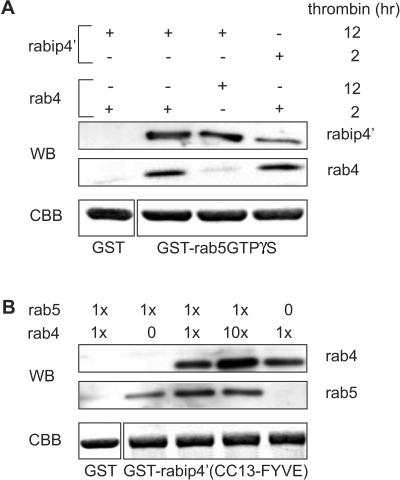
Figure 7.
rab4 and rab5 bind simultaneously to rabip4′. (A) GSTrab5 (loaded with GTPγS) and GST were immobilized on GSH beads and incubated with rabip4′ (CC13-FYVE). After washing, a second incubation was performed with rab4-GTPγS at a molar ratio rab5:rab4 of 5. Bound proteins were eluted, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and analyzed by Western blotting by using antibodies against rabip4′ (SN570) and rab4 (8091). Then, 0.5% of GSTrab5 and GST was loaded on a SDS-PAA gel and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) to control for input in the assays. rab4 bound to the GSTrab5 beads in the presence rabip4′, but not to GST beads when these were incubated with rabip4′. Extending the thrombin cleavage time of GSTrab4 from 2 to 12 h inactivates GTPγS-loaded rab4 and reduced rab4-binding to background level. (B) GSTrabip4′(CC13-FYVE) and GST were immobilized on GSH beads and first incubated with rab5-GTPγS. After washing, increasing amounts of rab4-GTPγS (x stands for 50 μg) were added and beads were further incubated. Bound proteins were eluted, resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against rab4 (8091) and rab5 (4F11). CBB staining shows that similar amounts of GSTrabip4′ (CC13-FYVE) and GST have been used in each reaction (1% of the input). Note that addition of a 10-fold molar excess of rab4 does not compete out bound rab5.