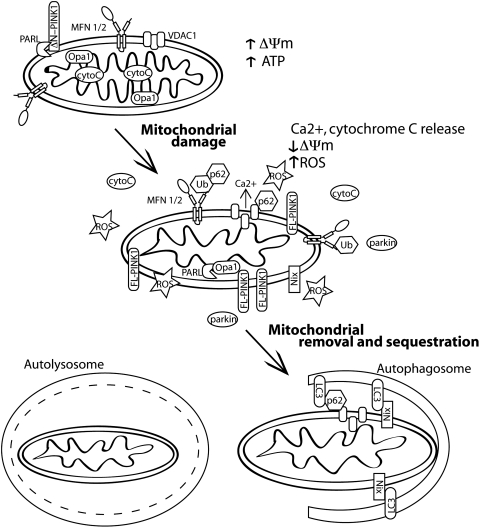
FIG. 3.
Regulation of mammalian mitophagy. When mitochondria become damaged, they are characterized by reduced membrane potential, they release calcium and cytochrome C and generate reactive oxygen species (ROS). Nonfunctional mitochondria are then removed by mitophagy to alleviate ROS and cytochrome C release into the cytosol and prevent apoptosis. There are several identified pathways to mitophagy activation. Nix is an outer mitochondrial membrane protein that binds to LC3 to promote mitochondrial engulfment by autophagic membranes. Another pathway induced by mitochondrial depolarization occurs when full length PINK1 (FL-PINK1) is no longer proteolysed and accumulates on the outer mitochondrial membrane. Increased levels of membrane-associated PINK1 recruit parkin to the mitochondria. Parkin ubiquitinates mitochondrial substrates, including VDAC and MFN. These ubiquitin modified substrates are recognized by the adaptor protein p62 and are trafficked to autophagosomes and eventually are degraded in lysosomes.