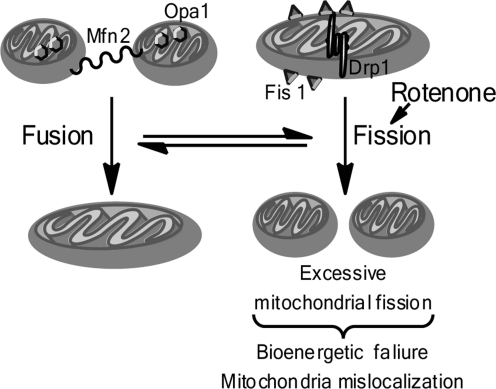
FIG. 1.
Dysregulated mitochondrial dynamics in Parkinson's disease toxin models. Dynamic balance between mitochondrial fission and fusion is required for normal cell homeostasis and function. Mitochondrial fusion occurs when mitofusion proteins (Mfn) link the outer mitochondrial membranes of two separate mitochondria, and the protein Opa1, which resides in the inner mitochondrial membrane, facilitates fusion of the inner mitochondrial membranes, resulting in the fusion of one mitochondria from two. Mitochondrial fission occurs when the fission protein Fis1 demarks the outer mitochondrial membrane, and by interaction with Drp1, promotes the fission of a single mitochondria into two individual mitochondria. Excessive mitochondria fusion is detrimental to cell survival, and rotenone promotes aberrant mitochondrial fusion.