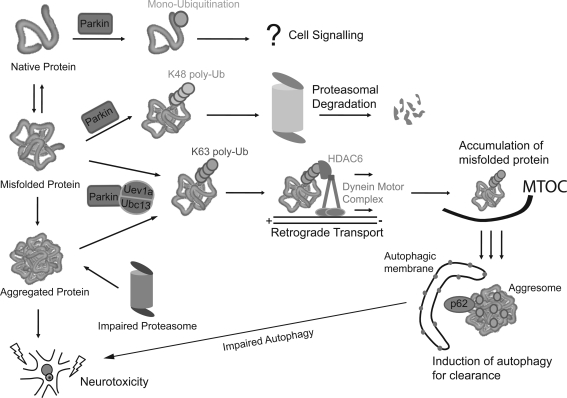
FIG. 4.
Parkin is a multifunctional ubiquitin ligase. Parkin is a unique E3 enzyme capable of mediating various types of ubiquitin (Ub) modification on its substrates that would result in different outcomes. Parkin-mediated monoubiquitination is thought to fulfill cellular signaling roles, whereas parkin-mediated K48-linked polyubiquitination is responsible for substrate degradation via the proteasome. On the other hand, parkin-mediated K63-linked polyubiquitination of substrates promotes aggresome formation through the recruitment of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) and p62 and also facilitates their subsequent clearance by autophagy. Although aggresome formation may be a cytoprotective response against proteasome dysfunction, their co-ordinated clearance by autophagy is presumably important to limit their growth. In the event of autophagy impairment, unregulated aggresome growth could become detrimental for neuronal survival.