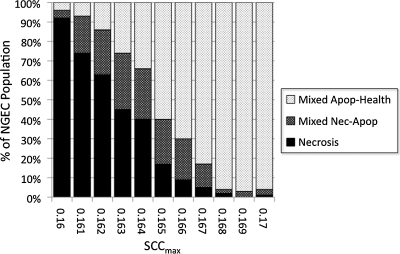
FIG. 5.
Parameter sweep of maximum stress clearance capability (SCCmax) between 0.160 and 0.170 with full feedings, bacteria, and no goblet cells (+Bact/−GC). Bacterial agents were added to the necrotizing enterocolitis agent-based model, and a series of simulations was performed for SCCmax values between 0.160 (32% AbSCCmax) and 0.170 (34% AbSCCmax) at intervals of 0.001 (n=100 simulation runs). There was an expected greater severity of outcome for each value of SCCmax at each value of SCCmax with the threshold for the absence of the Necrosis (Nec) outcome shifted from SCCmax 0.163 in the −Bact/−GC group to an SCCmax range of around 0.169 to 0.170. Furthermore, the Apoptosis (Apop) outcome disappeared in all simulation runs. Our interpretation is that bacterial activation of the pathogen-associated and damage-associated molecular pattern signaling pathways (represented in the NEC ABM by Toll-like receptor-4) provides a group-separating selection pressure on apoptotic neonatal gut endothelial cells (NGECs) to either progress to necrosis or “escape” toward recovery.