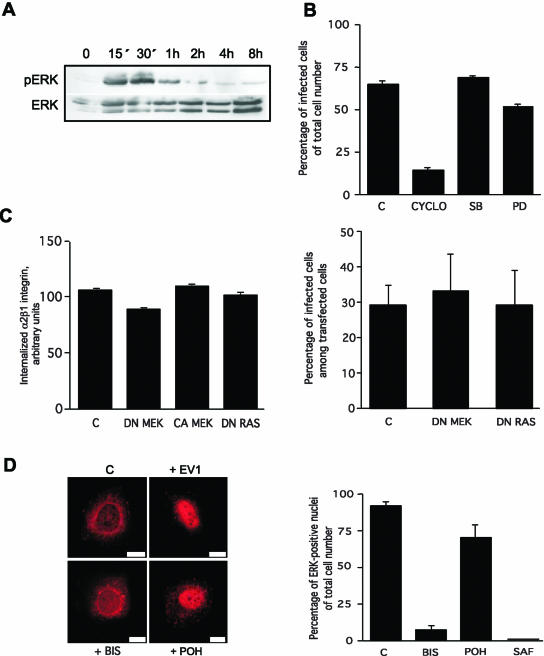
Figure 5.
Binding of α2β1 integrin to EV1 induces the phosphorylation of ERK MAP kinase in a PKCα activity-dependent manner. (A) ERK is transiently phosphorylated <15 min after α2β1 integrin binding to EV1 and the phosphorylation lasts ∼1 h (Western blot). (B) Inhibitors of ERK activation (PD) and p38 kinase (SB) do not inhibit infection in contrast to methyl β-cyclodextrin (CYCLO), an inhibitor of cholesterol metabolism and caveolae. (C) Transient transfections with cDNAs encoding the dominant negative MEK (DN MEK) or dominant negative Ras (DN Ras) do not inhibit α2β1 integrin internalization or infection. Constitutively active MEK (CA MEK) does not increase the internalization of α2β1 integrin either. (D) ERK is translocated to the nucleus 4 h p.i. The general PKC inhibitor bisindolylmaleimide (5 μM, BIS) inhibits the nuclear translocation of ERK, unlike a Ras inhibitor, perillyl alcohol (500 μM, POH). Quantification of ERK positive nuclei after treatments with bisindolylmaleimide (BIS), another PKC inhibitor safingol (10 μM, SAF) or Ras inhibitor (POH). Error bars show SE values (B and C: the graph on the left, D) or 95% confidence limits (C: the graph on the right).