Figure 10.
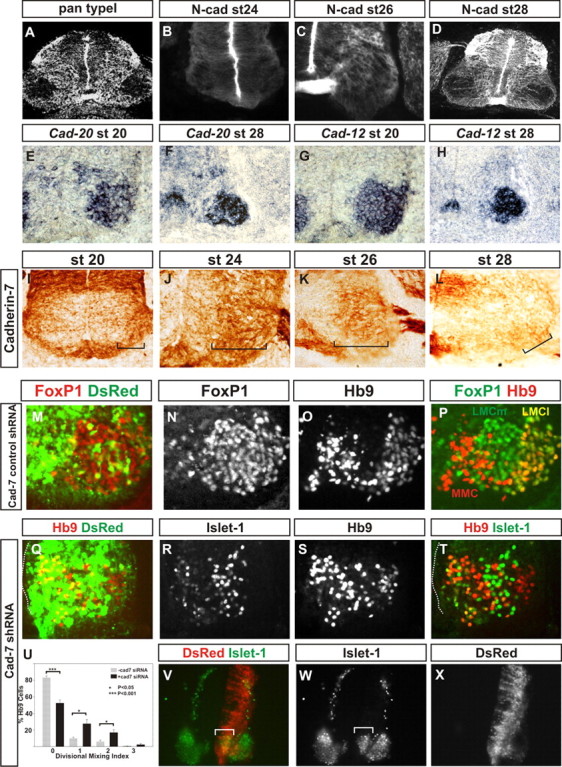
Pan-motor neuron type II cadherin expression and cadherin-7 siRNA restricts LMC neuron migration and divisional segregation. A, Pan type I cadherin immunolabeling at st28. B–D, N-cadherin immunoreactivity at st24 (B), st26 (C), and st28 (D). E, F, Cad-20 in situ hybridization in the ventral horn at st20 (E) and at caudal lumbar regions of st28 (F). G, H, Cad-12 in situ hybridization in the ventral horn at st20 (G) and at caudal lumbar regions of st28 (H). I–L, Cad-7 immunohistochemistry in the ventral spinal cord at st20 (I) and in the ventral horn at HH st24 (J), st26 (K), and st28 (L). Cad-7 appears to be expressed in the majority of LMC neurons during their migration (I–K) and is weakly expressed in only a small subset of motor neurons subsequently (L). M–P, Cad-7 control shRNA expression. Foxp1 (M, N, P), a pan-LMC marker, and Hb9 immunoreactivity (O, P) show normal segregation and positioning of LMCl, LMCm, and medial motor column following control shRNA expression, marked by dsRed fluorescence in M. Q–U, Cad-7 shRNA perturbs LMC divisional segregation. Q–T, HB9 (Q, S, T) and Islet-1 (R, T) immunohistochemistry at st28 following expression of cad-7 shRNA revealed by dsRed fluorescence (Q). Q, T, Dotted lines, Ventricle surface. Note that there are motor neurons close to the ventricle surface. U, Divisional mixing index following cad-7 shRNA expression compared with cells that had not acquired the construct (p < 0.001 for the 0 bin, p < 0.05 for the 1 and 2 bins, Student's t test; χ2 analysis, p < 0.001 2df). V–X, Islet-1 immunohistochemistry (V, W) at st24 reveals a perturbation of LMCm migration following cad-7 shRNA expression (V, W, bracket) revealed by dsRed fluorescence (V, X); note the paucity of dsRed fluorescence in the lateral LMC.
