Figure 5.
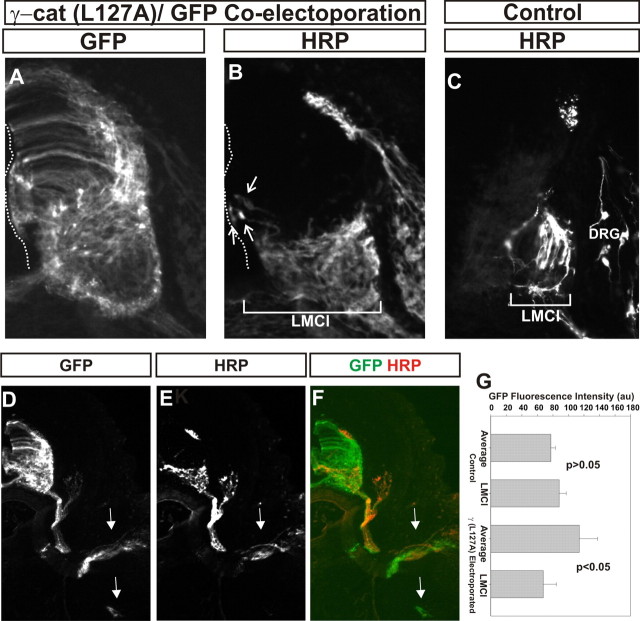
Motor neuron projections appear normal following γ-catenin (L127A) expression. GFP and γ-catenin(L127A) were coelectroporated at stage 18 and HRP was injected into the dorsal limb at stage 29. A, B, GFP (A) and HRP (B) immunofluorescence in one section. B, Arrows, Motor neurons close the ventricular surface that projected into the dorsal limb. A, B, Dotted lines, Ventricle surface. C, HRP retrograde labeling in control embryos. B, C, Bars, Mediolateral extent of retrogradely labeled motor neurons. Note that the bar in B is more than twice as long as the one in C. D–G, GFP immunofluorescence is more intense medially in the spinal cord than in controls following γ-catenin(L127A)/GFP coelectroporation. D, F, GFP immunofluorescence. E, F, HRP immunofluorescence. G, Quantitation of average GFP immunofluorescence in the spinal cord versus that found in the lateral LMC following GFP or γ-catenin(L127A)/GFP coelectroporation. GFP fluorescence is lower in the lateral ventral horn following γ-catenin(L127A) expression, consistent with a defect in motor neuron migration. D–F, Arrows, Motor axon tracks to dorsal and ventral limb. Note that GFP is present in both, whereas HRP immunofluorescence is exclusively in the dorsal limb tracks. Error bars are SEM.