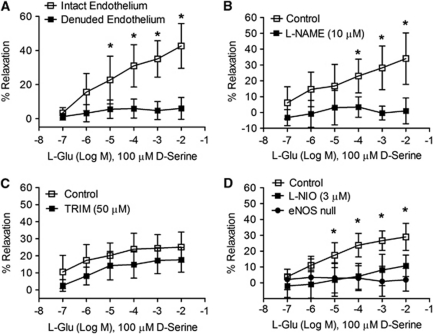
Figure 4.
Vasodilation by glutamate and -serine requires intact endothelium and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS). (A) Removal of the endothelium isolated middle cerebral arteries (MCAs) an air bolus significantly attenuated smooth muscle relaxation caused by incremental glutamate concentrations in the presence of 100 μmol/L -serine (n=6). (B) N-nitro--arginine methyl ester (-NAME; 10 μmol/L) blocked concentration-dependent vasodilation caused by glutamate and -serine (n=6). (C) Glutamate/-serine-induced MCA relaxation is not affected by the neuronal NOS inhibitor, 1-(2-(trifluoromethylphenyl)) imidazole (TRIM; 50 μmol/L). (D) N5-(1-iminoethyl)--ornithine (-NIO; 3 μmol/L), an eNOS-selective antagonist, and eNOS deletion prevented MCA relaxation by incremental glutamate increases in the presence of 100 μmol/L -serine (n=6). Data are presented as mean±s.d.; *P<0.05 using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) for repeated measures and Bonferroni post-hoc test.