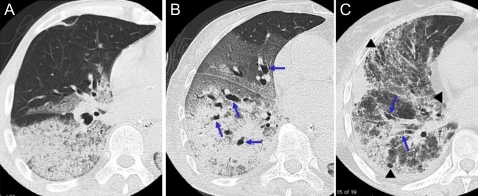
Figure 2.
High-resolution CT findings correlated with pathology. (A) High-resolution CT findings corresponding to exudative phase of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). HRCT scan at the level of right middle lobe shows dependent airspace consolidation without traction bronchiectasis and non-dependent areas of sparing. The patient was a 68-year-old man with ARDS due to Streptococcus pneumonia. (B) High-resolution CT findings corresponding to fibroproliferative phase of ARDS. HRCT scan at the level of right lower lobe shows extensive airspace consolidation and ground-glass attenuation associated with traction bronchiectasis (arrows). The patient was an 84-year-old woman with ARDS due to sepsis. (C) High-resolution CT findings corresponding to fibrotic phase of ARDS. HRCT scan at the level of right inferior pulmonary vein shows extensive ground-glass attenuation associated with traction bronchiectasis (arrows), coarse reticulation and cystic changes (arrowheads). The patient was a 65-year-old woman with ARDS due to viral pneumonia. (Sequential changes of HRCT findings were shown in the supplemental figure.)