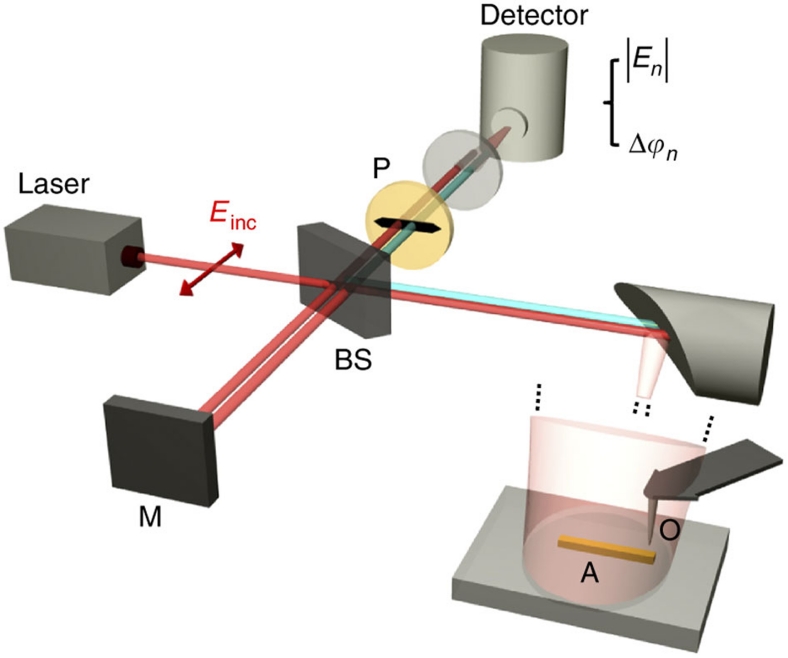
Figure 2. Set-up for verifying surface-enhanced elastic light scattering.
The set-up comprises a scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope (s-SNOM, from Neaspec GmbH), which is based on an atomic force microscope (AFM). The apex of a conventional Si tip acts as the scattering object (O). The antenna and tip are illuminated at an angle of about 50° relative to the surface normal with the focused beam of a CO2 laser operating at 11.1 μm. The polarization of the illuminating beam Einc is parallel to the long axis of the metal rod (s-polarized light). The field backscattered by the antenna (A) and the tip (O) is collected and detected with a pseudo-heterodyne interferometer (M denotes the reference mirror and BS the beamsplitter). The polarizer P ensures that s-polarized light is detected. To obtain a modulation of the distance between tip and antenna, the tip is oscillating vertically at a frequency Ω=300 KHz and with an amplitude of 70 nm. Demodulation of the detector signal at a higher harmonic nΩ yields the amplitude and phase signals |En| and Δϕn.