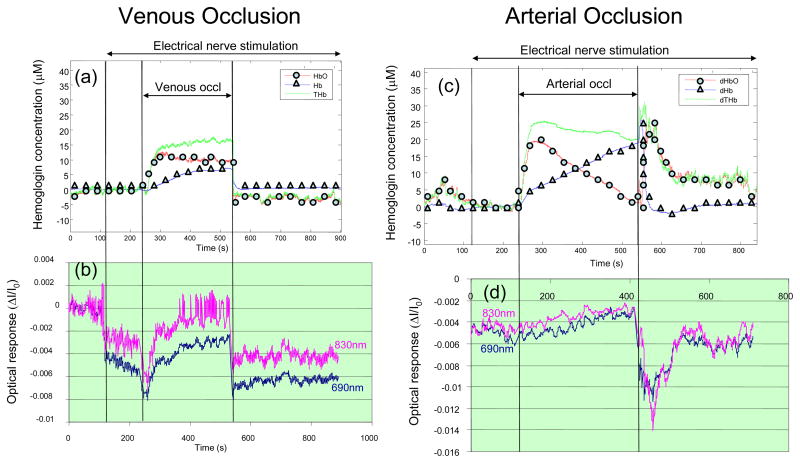
Fig. 4.
Effect of venous occlusion on (a) the average tissue concentrations of oxy-hemoglobin (HbO), deoxy-hemoglobin (Hb), and total hemoglobin (THb), and (b) the amplitude of the optical response to nerve stimulation at the two wavelengths of 690 and 830 nm. Effect of arterial occlusion on (c) the average tissue concentrations of oxy-hemoglobin (HbO), deoxy-hemoglobin (Hb), and total hemoglobin (THb), and (d) the amplitude of the optical response to nerve stimulation at the two wavelengths of 690 and 830 nm. The vascular occlusion is caused by a pressure applied by a pneumatic cuff to the upper arm (50 mmHg for venous occlusion, 220 mmHg for arterial occlusion) during the time indicated in the figure.