Figure 2.
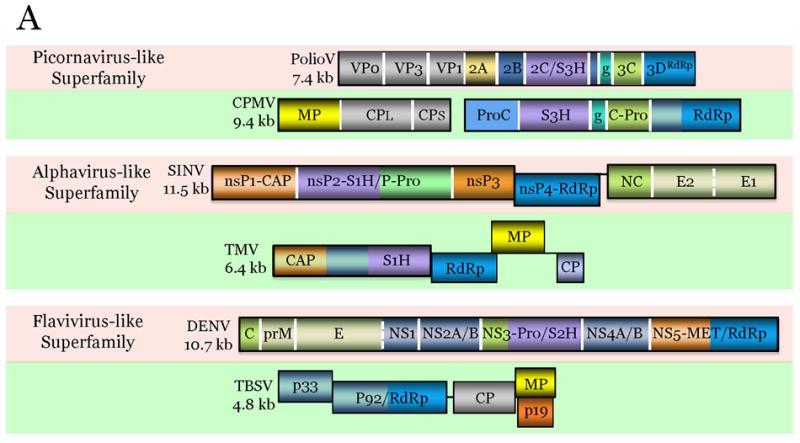
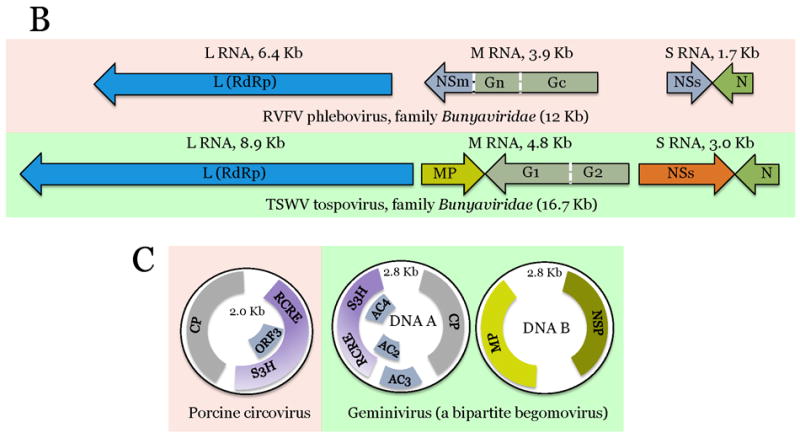
Comparison of genome architectures of related plant and animal viruses: The housekeeping and interactive gene modules.
The virus genes are drawn as boxes approximately to scale. For each pair of animal (pink background) and plant (green background) viruses, the homologous genes are shown in the same color. Gene designations: VP, virus protein; S3H, superfamily 3 helicase; g, virus protein, genome-linked; RdRp, Rna-dependent RNA polymerase; MP, movement protein; CP, capsid protein; ProC, protease cofactor; C-Pro, cysteine protease; nsP, non-structural protein; CAP, capping enzyme; S1H, superfamily 1 helicase; P-Pro, papain-like protease; NC, nucleocapsid protein; E, envelope protein; C, nucleocapsid protein; prM, pre-membrane protein; NS, non-structural protein; Pro, protease; S2H, superfamily 2 helicase; MET; methyltransferase; G, glycoprotein; N, nucleocapsid protein; RCRE, rolling-circle replication endonuclease; NSP, nuclear shuttle protein. Virus abbreviations: PolioV, Poliovirus; CPMV, Cowpea mosaic virus; SINV, Sindbis virus; TMV, Tobacco mosaic virus; DENV Dengue fever virus; TBSV, Tomato bushy stunt virus; RVFV, Rift valley fever virus; TSWV, Tomato spotted wilt virus.
