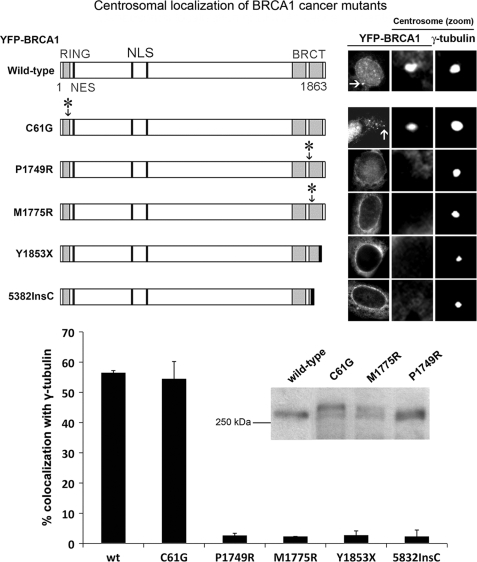
FIGURE 1.
Cancer-associated BRCT mutations prevent BRCA1 centrosome localization. Shown is a schematic diagram showing the organization of BRCA1 protein domains (the RING and BRCT domains, the NLS, and the NES) as well as cancer-associated mutations. YFP-tagged BRCA1 cancer-associated mutants were transfected into MCF-7 breast cancer cells and analyzed for co-localization with the centrosome-component γ-tubulin by immunofluorescence microscopy. Representative cell images of YFP-BRCA1 localization are shown in the right-hand panel, in addition to close-up images of the centrosomes, with staining of BRCA1 and γ-tubulin. Cells expressing YFP-tagged BRCA1 were scored for co-localization with the centrosome. Scoring results were obtained from at least three independent experiments, each with at least 100 cells scored (mean ± S.D. (error bars)). Integrity of the BRCA1 point mutants was validated by Western blot (see inset).