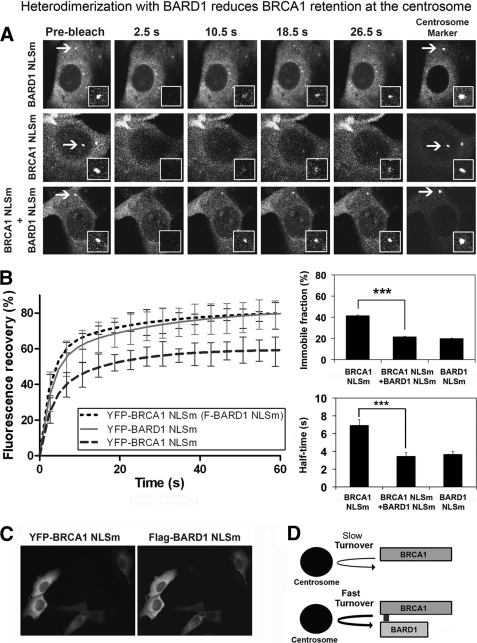
FIGURE 7.
Dimerization with BARD1 reduces BRCA1 retention at the centrosome. A, FRAP analysis was performed on YFP-tagged BRCA1 NLS mutant, BARD1 NLS mutant, and BRCA1 NLS (+FLAG-BARD1 NLS mutant) in transfected MCF-7 cells. Centrosome was marked by co-transfection with RFP-pericentrin C241. Note that co-expression of BRCA1 and BARD1 normally results in nuclear entrapment, whereas expression of NLS-mutated forms permits live cell analysis of the BRCA1-BARD1 heterodimer in the cytoplasm and at centrosomes. Centrosome fluorescence was photobleached, and fluorescence recovery was measured. Representative pre- and postbleach images are shown for each protein. The insets show higher magnification views of the target area. B, corresponding recovery curves are shown for each of the above proteins. The t½ (half-time ± S.E. (error bars)) and immobile fraction (percentage ± S.E.) are also shown (***, p < 0.001). The data show that BARD1 co-expression increases the rate of BRCA1 dynamics and reduces its retention at centrosomes. C, co-expression of BRCA1 and BARD1 was verified by immunofluorescence microscopy in parallel to FRAP experiments. pYFP-BRCA1 NLSm and pFLAG-BARD1 NLSm were co-transfected into MCF-7 cells, fixed with acetone/methanol and stained with anti-FLAG antibody (Sigma) and Hoechst dye. More than 98% of cells displayed co-expression. D, model showing that the heterodimeric form of BRCA1 (BRCA1-BARD1) has a faster exchange rate than monomeric BRCA1.