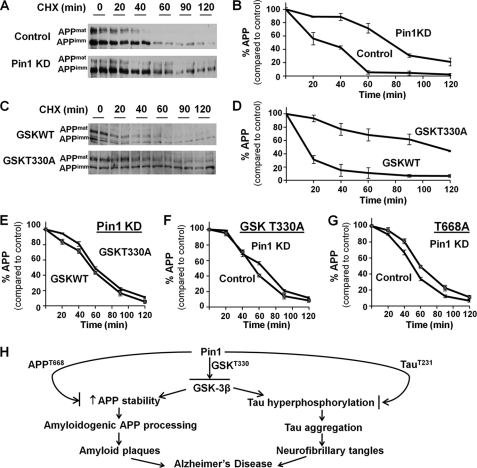
FIGURE 4.
Pin1 inhibits GSK3β to promote APP turnover. A and B, cells were treated with cycloheximide (CHX)for the indicated time and then subjected to Western blot for APP. When Pin1 was knocked down (Pin1 KD), APP stability was increased, and thus the rate of APP degradation slowed down. APPmat, mature form of APP; APPimm, immature form of APP. C and D, GSK3β T330A reduced the rate of APP degradation when compared with GSK3β WT. E, when Pin1 was knocked down, there was no difference in APP degradation with GSK3β WT or T330A. F, when cells were transfected with GSK3β T330A, Pin1 knockdown did not affect APP degradation. G, Pin1 did not affect the stability of the APP T668A mutant, which abolished the binding site for Pin1 or GSK3β on APP. H, model showing the role of Pin1 on the regulation of GSK3β, which regulates the downstream pathway on APP and Tau, modulating the pathogenesis of AD.