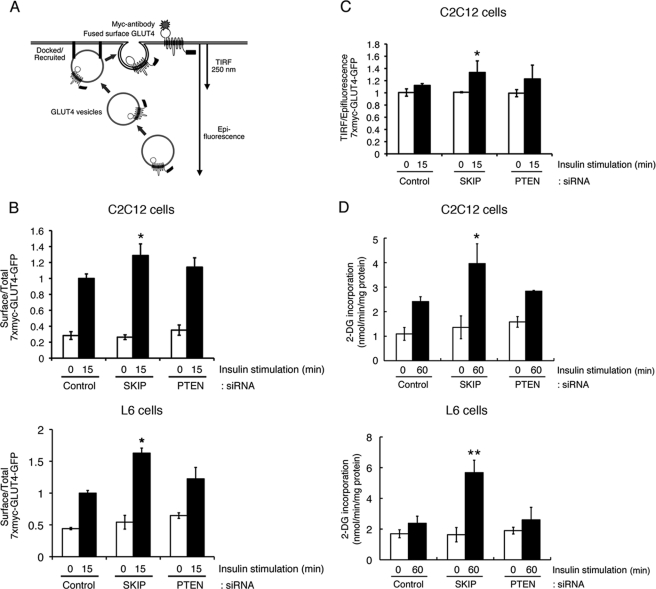
FIGURE 5.
SKIP regulates insulin-induced exocytosis of GLUT4 and glucose uptake. A, schematic model of the GLUT4 translocation assay. GLUT4 reporter fluorescence in the basal or insulin-stimulated cells was measured in the epifluorescence and TIRF modes. Translocation of GLUT4 at the cell surface was measured by immunofluorescence with anti-Myc antibody. B, SKIP negatively regulated insulin-dependent GLUT4 translocation. Surface-to-total distribution of GLUT4 reporter was analyzed in C2C12 or L6 cells expressing GLUT4 reporter. Cell surface GLUT4 reporter was analyzed by immunofluorescence with anti-Myc antibody. Cells were stimulated with insulin (100 nm) for 15 min. *, p < 0.05 (t test). C, SKIP negatively regulated docking and/or fusion steps of GLUT4 translocation in C2C12 cells. Quantification of GLUT4 at the plasma membrane was performed by TIRF microscopy. For each experiment, the data are normalized to the control siRNA-transfected cells. *, p < 0.05 (t test). D, insulin-dependent glucose uptake was increased by suppression of SKIP. C2C12 or L6 cells transfected with control-, SKIP-, or PTEN-directed siRNAs in combination with GLUT4 reporter were subjected to a 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG) uptake assay, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Cells were stimulated with insulin (10 nm) for 60 min. *, p < 0.05 (t test). Error bars, S.E.