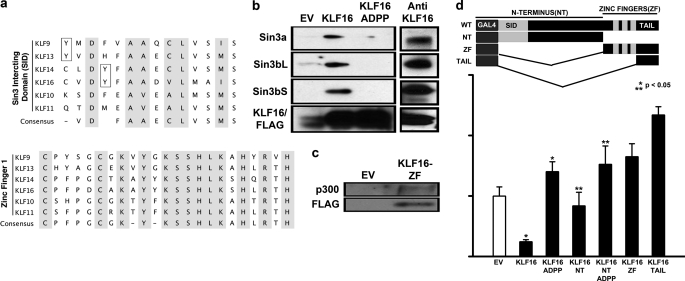
FIGURE 4.
KLF16 couples to different chromatin pathways involved in histone acetylation-deacetylation. a, upper panel, sequence alignment of the SID domain of BTEB-KLF9, -13, -14, and -16 reveals the discrepant position of tyrosine residues within (KLF14 and -16) and outside (KLF9 and -13) the minimal SID (shaded). Also shown are the SID domains of closely related TIEG-KLF10 and -11. Unlike KLF11, KLF16-SID does not contain a candidate phosphorylatable Ser/Thr residue. Lower panel, sequence alignment of the first zinc finger of all BTEB-KLFs. KLF16-ZF1 has high sequential homology to KLF11- and -13-ZF1 and also interacts with p300/HAT (completely conserved residues shaded). b, left panel, uterine cells transfected with either 5 μg of pCMV/FLAG vector, pCMV/FLAG-KLF16, or pCMV/FLAG-KLF16ADPP (Sin3-binding mutant) and 5 μg of either Sin3 isoforms for 48 h were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG-agarose beads. Immunocomplexes were analyzed by Western blot using either anti-Sin3a or anti-Sin3b. Sin3a as well as both Sin3b isoforms (long and short) were present in immunocomplexes obtained from cells transfected with FLAG-KLF16 but not from cells transfected with either the empty vector or Sin3-binding mutant FLAG/KLF16-ADPP. Right panel, immunoprecipitation of endogenous KLF16 was performed on uterine cells using an antibody to KLF16. Immunocomplexes were analyzed by Western blot using either anti-Sin3a or anti-Sin3b. Sin3a as well as both Sin3b isoforms (long and short) were detected in immunocomplexes formed by endogenous KLF16. c, uterine cells were cotransfected with 5 μg of FLAG-KLF16-ZF or FLAG-EV and 5 μg of p300. Immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-FLAG-agarose beads, and Western blot using anti-p300 showed that KLF16 bound p300/HAT via the ZF domain (d). Uterine cells were cotransfected for 48 h with either empty vector (pM), full-length, or mutation/deletion KLF16 constructs and Gal4-luciferase reporter vector. Luciferase activity normalized to lysate protein concentration showed that although full-length KLF16 and KLF16-N terminus repressed reporter expression 50% (*, **, p < 0.05, respectively), the repression was reversed when either full-length or N-terminal KLF16 constructs contained the ADPP mutation that abrogated Sin3a binding. Paradoxically, the C terminus and the C-terminal tail of KLF16 increased reporter expression.