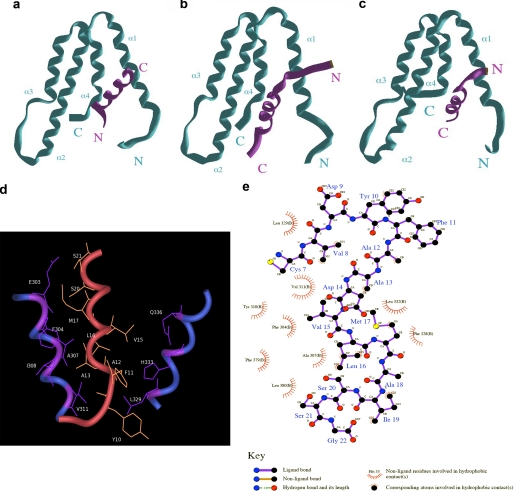
FIGURE 6.
Predictive structural model for the Sin3a-PHA2-KLF16 SID complex. a, MAD1-SID-PAH2 complex. The MAD1 SID α-helix adopts an N to C orientation within the hydrophobic pocket form by the four helices bundle of PAH2. b, HBP1-SID-PAH2 complex. The HBP1 SID α-helix adopts a reverse C to N orientation within the hydrophobic pocket formed by the four helices bundle of PAH2. c, KLF16 SID-PHA2 complex. The KLF16 SID α-helix adopts an HBP1-like N to C orientation within the hydrophobic pocket formed by the four helices bundle of PAH2. Similar experiments performed by docking of the KLF16 SID in a reverse MAD1-like orientation were not stable after MD simulation. d, close up view displaying the primary hydrophobic contacts that contribute to the KLF16 SID-PAH2 complex. e, simplified view of the most important bonds responsible for the formation and function of the KLF16 SID. This model predicts that modifications of Tyr-10, which contributes to the formation and/or stability of the KLF16 SID-PAH2 complex, may impact on the regulation of the silencing activity of this KLF protein.