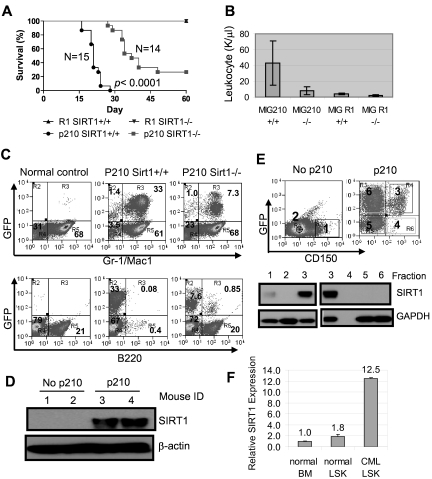
Figure 6.
SIRT1 knockout suppresses the development of CML-like disease in a mouse model. (A-B) Survival curves (A) for mice receiving 2.5 × 105 mononuclear cells transduced by BCR-ABL MIG210 vector (p210) or empty vector (R1) and total leukocyte counts (B) for mice at 18 days after transplantation. In R1-transduced mouse controls, there were 8 mice receiving SIRT1+/+ donor cells and 6 mice receiving SIRT1−/− cells. (C) BM cell lineage analysis in normal BALB/c (control) and mice receiving MIG210 transformed SIRT1+/+ or SIRT1−/− cells. (D) SIRT1 protein expression in total BM mononuclear cells from normal BALB/c and mice receiving MIG210-transformed SIRT1+/+ cells (n = 2 in each group). (E) BM progenitor cells from normal BALB/c and mice receiving MIG210-transformed SIRT1+/+ cells were enriched by EasySep to remove lineage cells and then sorted for GFP and CD150 expression. Bold numbers indicated the sorted fractions that were used for analysis of SIRT1 protein expression. GFP+CD150+ (fraction 3) cells were also loaded with fractions 1 and 2 from BALB/c mice for comparison. (F) SIRT1 mRNA levels in normal BALB/c BM and LSK cells compared with LSK cells purified from CML mice.