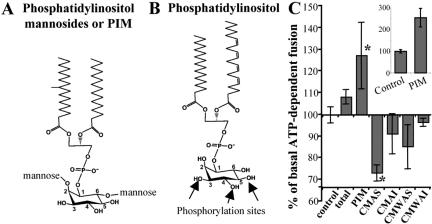
Figure 1.
Effects of mycobacterial lipids on early endosomal fusion. Structures of phosphatidylinositol mannosides PIM (A) and a typical mammalian phosphatidylinositol (B). PIM is glycosylated with single mannose residues at positions 2 and 6 of the inositol ring, whereas positions 3, 4, and 5 are unsubstituted. In eukaryotic cells, phosphatidylinositol can be phosphorylated at the positions 3, 4, or 5 on the inositol headgroup as indicated by arrows. (C) Early endosomal fusion was carried out in the presence of 40 μg/ml mycobacterial lipids, and 2 mg/ml cytosol, for 1 h at 37°C. CMAS and CMAI: lipids soluble in chloroform/methanol (2/1) (CM) and soluble (AS) or insoluble (AI) in acetone. CMWAS and CMWAI: lipids soluble in chloroform/methanol/water (10/10/3) (CMW) and soluble (AS) or insoluble (AI) in acetone. Total, unfractionated lipids extracted from M. tuberculosis. Inset, stimulatory effect of PIM upon preincubation of PIM with cytosol and ATP, before the initiation of endosomal fusion. Shown is the percentage of ATP-dependent fusion (1 mg/ml cytosol) in the presence or absence of PIM preincubated with cytosol and ATP-regenerating system for 20 min. Bars, SEM asterisk, p < 0.05 (ANOVA).