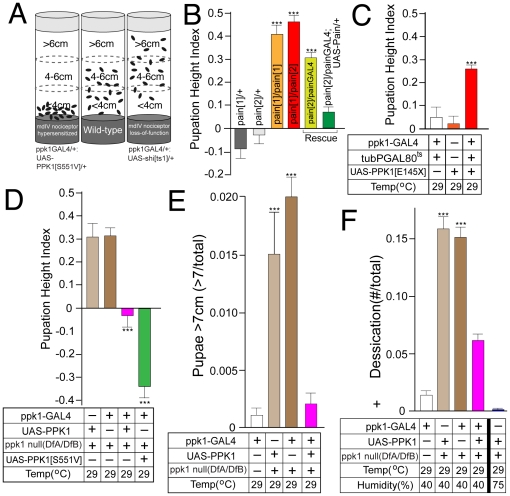
Figure 5. Larval aversion to dry surfaces requires both the DEG/ENaC subunit PPK1 and the TRP channel Pain.
(A) Schematic depiction summarizing opposing mdIV nociceptor gain-of-function and loss-of-function phenotypes. (B) pain mutant alleles showed increased pupation height phenotype that was rescued by transgenic expression of wild-type Pain protein. (C) Transgenic expression of the dominant-negative PPK1[E145X] isoform after 96 h AEL caused an increase in pupation height similar to that observed with mdIV nociceptor inactivation. (D) ppk1 null mutant larvae displayed an increase in pupation height that was rescued by transgenic expression of wild-type PPK1 or the constitutively-active PPK1[S551V] isoform in mdIV nociceptor neurons. (E) Fraction of total larvae pupating in the top regions of the vial(>7 cm) was significantly increased in ppk1 null mutants and rescued by mdIV-specific expression of wild-type PPK1. (F) Fraction of total larvae displaying the lethal desiccated larval phenotype was significantly increased in ppk1 null mutant larvae. Larval desiccation was rescued by transgenic expression of wild-type PPK1 or by growth at high humidity(75%). All vials were shifted to 29°C/40% humidity at 96 h AEL unless otherwise indicated. Error bars represent SEM with n≥15 for all values. ***P<.0001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey posttest.