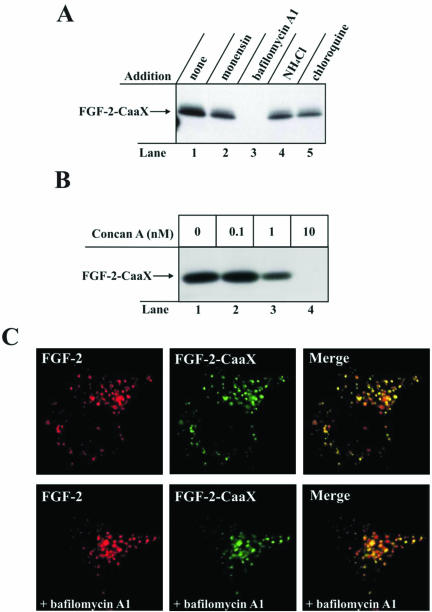
Figure 5.
Effect of various inhibitors of lumenal acidification of intracellular vesicles on the ability of FGF-2-CaaX to become prenylated in vivo. (A) NIH/3T3 cells were pretreated as in Figure 2A and then treated for 6 h with heparin and FGF-2-CaaX in the absence (lane 1) or presence of 1 μM monensin (lane 2), 10 nM bafilomycin A1 (lane 3), 20 mM NH4Cl (lane 4), or 100 μM chloroquine (lane 5). After lysis, cellular material was analyzed as in Figure 2A. (B) NIH/3T3 cells were pretreated as in Figure 2A and then treated for 6 h with heparin and FGF-2-CaaX in the absence (lane 1) or the presence of increasing concentrations of concanamycin A (lanes 2-4). After lysis, cellular material was analyzed as in Figure 2A. (C) FGF-2 conjugated to Cy3 maleimide and FGF-2-CaaX conjugated to Alexa 488 maleimide were added to NIH/3T3 cells overexpressing FGFR1 and incubated for 2 h at 37°C. In some cases, the cells were pretreated with 10 nM bafilomycin A. The cells were then fixed and analyzed by confocal microscopy.