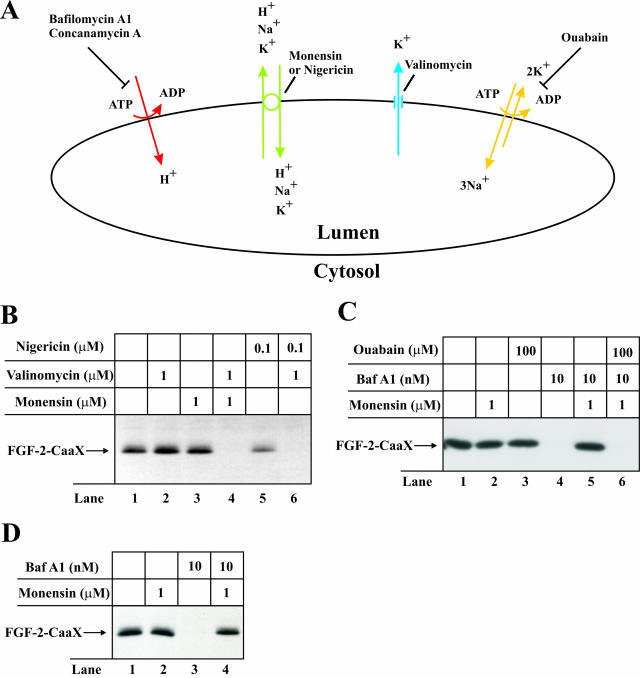
Figure 6.
Effect of depolarization and repolarization of the membrane of intracellular vesicles on the ability of FGF-2-CaaX to become prenylated in vivo. (A) H+ are pumped from the cytosol into the lumen of the vesicles by V-type H+-ATPase (red) lowering lumenal pH and creating a membrane potential (positive inside the vesicle). The membrane potential is partly compensated for by the influx of Cl- counterions (not indicated). Inhibition of vacuolar proton pumps by bafilomycin A1 or concanamycin A causes depolarization of the membrane. Monensin or nigericin (green) exchange H+ accumulated in the vesicle lumen for K+ present in the cytosol, which raises the lumenal pH but does not dissipate the membrane potential. When both monensin (or nigericin) and valinomycin (blue) are present, efflux of K+ from the lumen to the cytosol results in the dissipation of the membrane potential. Endosomes also contain Na+/K+-ATPase (yellow), which is usually inactive because of deficiency in lumenal K+. In the presence of monensin (or nigericin) lumenal K+ can be replenished (in exchange for Na+) leading to reactivation of the Na+/K+-ATPase and regeneration of the membrane potential even when V-type H+-ATPase is blocked. Under these conditions, treatment with ouabain (inhibitor of Na+/K+-ATPase) will lead again to depolarization of the membrane. (B) CPAE cells were pretreated as in Figure 2A and then treated for 6 h with heparin and FGF-2-CaaX in the absence (lane 1) or presence of valinomycin (lane 2), monensin (lane 3), nigericin (lane 5), or a combination of valinomycin and either monensin (lane 4) or nigericin (lane 6). After lysis, cellular material was analyzed as in Figure 2A. (C) NIH/3T3 cells were pretreated as in Figure 2A and then treated for 6 h with heparin and FGF-2-CaaX in the absence (lane 1) or presence of monensin (lane 2), ouabain (lane 3), bafilomycin A1 (lane 4), or a combination of both bafilomycin A1 and either monensin (lane 5) or monensin and ouabain (lane 6). After lysis, cellular material was analyzed as in Figure 2A. (D) CPAE cells were pretreated as in Figure 2A and then treated for 6 h with heparin and FGF-2-CaaX in the absence (lane 1) or presence of monensin (lane 2), bafilomycin A1 (lane 3), or a combination of both monensin and bafilomycin A1 (lane 4). After lysis, cellular material was analyzed as in Figure 2A.