Fig. 1.
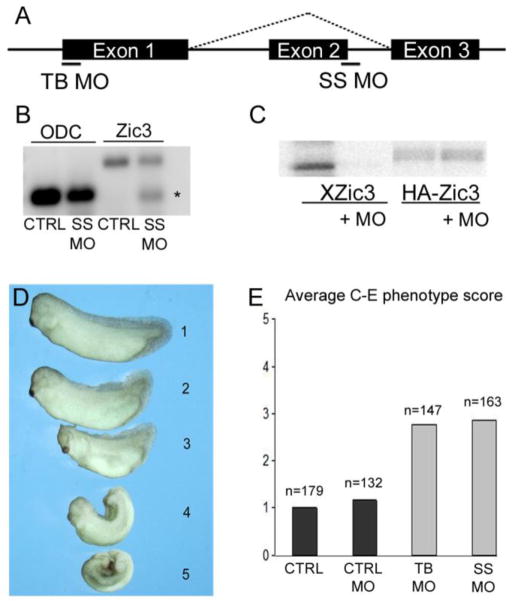
Knockdown of Zic3 disrupts axial development in Xenopus. (A) Schematic of zic3 exon-intron structure showing translational-blocking (TB) and splice site blocking (SS) morpholino target sites. (B) RT-PCR analysis of zic3 in control (CTRL) and SS MO injected embryos. Asterisk denotes product that lacks exon 2. The top band is the full-length zic3 product. ODC was used as a loading control. (C) In vitro transcription-translation using Xenopus zic3 (Xzic3) or human HA-ZIC3 expression plasmids in the presence or absence of Zic3 TB MO.
(D) Scaling system used to score Xenopus Zic3 morphant phenotypes that ranged from normal (1) to severe dorsal flexion with neural tube defect (5). (E) Average scores of control (CTRL), control morpholino (CTRL MO), Zic3 translational-blocking MO (TB MO), and Zic3 splice site morpholino (SS MO) injected embryos. Number of embryos (n) scored is shown above each injection group.