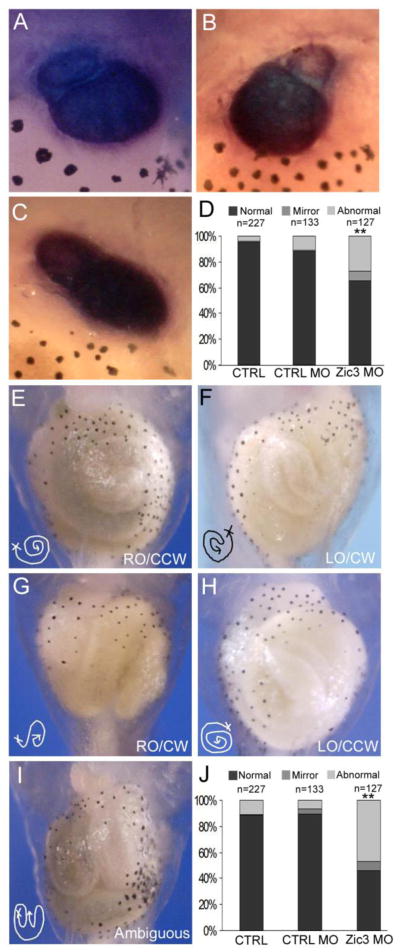
Fig. 5.
Reduction of Zic3 expression results in heart and gut abnormalities. (A–C) Ventral view of troponin WISH staining of the heart in Xenopus stage 46 embryos. (A) Normal heart looping with outflow tract from the right side. (B) Mirror phenotype, with outflow tract from the left side. (C) Abnormal heart looping, with no clear laterality of the outflow tract position. (D) Quantification of heart looping phenotypes in controls and Zic3 morphants. (E–I) Ventral view of Xenopus gut coiling in control and Zic3 morphant stage 46 embryos. (E) Normal gut coiling, right origin (RO) and counter-clockwise coil (CCW) direction. (F) Mirror gut coiling phenotype, left origin (LO) and clockwise coil (CW) direction. (G) Normal gut origin with reversed coil direction, clockwise. (H) Mirror gut origin, left side, with normal coil direction, counter-clockwise. (I) Abnormal gut coiling phenotype, no clear origin or coil direction. (J) Quantification of gut coiling phenotypes in control and Zic3 morphants. **p<0.01 by Fisher’s exact test; statistical significance was determined through comparison of control morphants with Zic3 morphants.