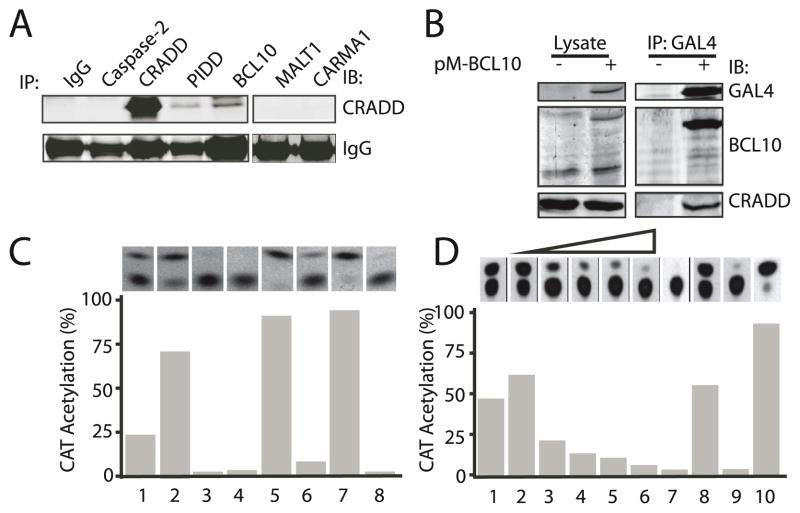
Figure 1. CRADD interacts with BCL10 through the CARD domain and prevents CARMA1 binding to BCL10.
(A) CRADD and BCL10 co-immunoprecipitate. Protein complexes precipitated from primary spleen cells with antibodies to the indicated proteins (IP) were immunoblotted (IB) with anti-CRADD antibody.
(B) Association between epitope-tagged BCL10 and cellular CRADD protein. 293T cells were transfected with pM-BCL10, which expresses a Gal4BCL10 fusion protein. Lysates (left panel) or immune complexes precipitated with anti-Gal4 antibodies (right panel) from control (−) or transfected (+) cells were subjected to western blot analysis (IB) using antibodies to the indicated proteins.
(C) CRADD interacts with BCL10 via the CARD domain. Mammalian two-hybrid assay in 293 T cells expressing proteins with DNA binding (DB) and trans-activation (AD) domains: DB-CRADD + AD-BCL10 (1); DB-CRADDCARD + AD-BCL10 (2); DB-CRADDDEATH + AD-BCL10 (3); DB-CRADD + AD-MALT1 (4); DB-p53 + AD-T antigen (5); DB-p53 + AD-Polyoma coat protein (6); DB-AD-M3-vp16 (7) and chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT) reporter plasmid only (8). CAT activity indicative of protein interaction was assayed by thin layer chromatography (upper panel) and quantified by densitometry (lower panel).
(D) CRADD competitively interferes with interactions between BCL10 and the CARMA1 CARD domain. Two-hybrid assay of protein interactions in 293T cells expressing: DB-CRADD + AD-BCL10 (1); DB-CARMA1CARD + AD-BCL10 + increasing amounts (0– 40 μg) of Myc-CRADD (2–6); 10 μg Myc-CRADD (7); DB-p53 + AD-T antigen (8); CAT reporter only (9); and DB-AD-M3-vp16 (10).