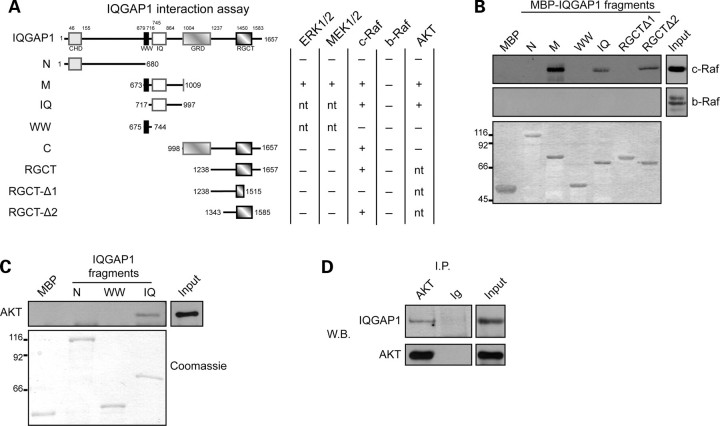
Figure 5.
IQGAP1 interacts with c-Raf, MEK1/2, ERK1/2, and AKT in the heart. (A) MBP-fused recombinant IQGAP1 fragments (N, N-terminal fragment; M, middle fragment; C, C-terminal fragment; IQ, IQ domain-containing fragment; WW, WW domain-containing fragment; RGCT, RGCT domain-containing fragment; RGCT-Δ1, RGCT domain-containing fragment deletion mutant 1; RGCT-Δ2, RGCT domain-containing fragment deletion mutant 2). Columns on the right indicate the capability of each fragment to interact (+) or not (−) with the indicated proteins as evaluated by pull-down assays (nt, not tested). (B and C) Pull-down experiments with MBP-fused IQGAP1 fragments were used to map the c-Raf (B) and AKT (C) binding region on IQGAP1. This interaction was revealed by western blotting (upper panels). Recombinant proteins used in the pull-down assay were visualized by Coomassie staining (lower panel). (D) AKT and IQGAP1co-immunoprecipitation was detected by western blotting. Input: heart total protein extract. Input was analysed in the same blot; however, a lower exposure is shown to allow a precise detection of the reference band. Figures showed representative pull-down and immunoprecipitation analyses that have been performed at least three times with comparable results.