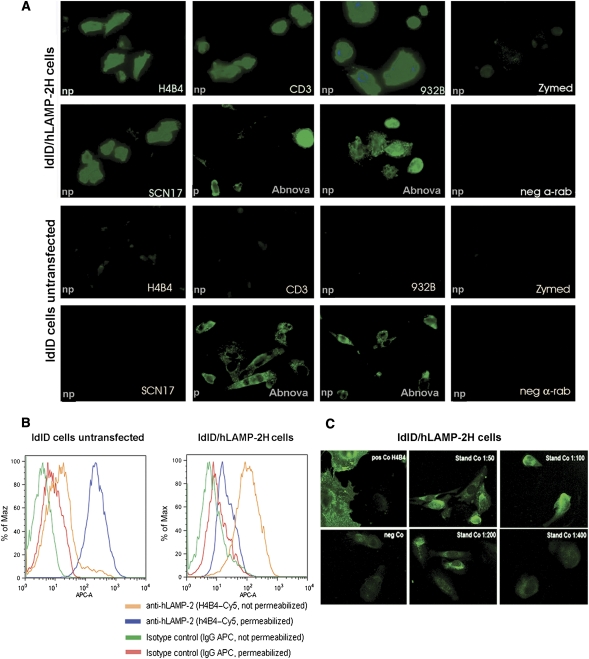
Figure 3.
Indirect immunofluorescence on ldlD cells stably expressing hLAMP-2 on the cell surface (ldlD/hLAMP-2H). (A) ldlD cells were transfected with full-length hLAMP-2 cDNA with a tyrosine to histidine mutation in the cytoplasmic lysosomal retrieval signal. Stable transfectants were sorted by flow cytometry for uniform expression of the transgene and stained with monoclonal (CD3) and polyclonal (932B) antibodies to hLAMP-2 generated by M. Fukuda as well as commercially available monoclonal (H4B4) and polyclonal anti-LAMP-2 antibodies (SCN17 and Abnova). All of the antibodies bound to hLAMP-2 on the surface of nonpermeabilized transfected cells (np). The commercial anti-hLAMP-2 cross-reacted with hamster LAMP-2 in transfected and untransfected cells especially after permeabilization (p). CD3 and 932B were the only antibodies that did not cross-react with hamster LAMP-2. A polyclonal antibody to rat LAMP-2 (Zymed Laboratories) and secondary antibody alone fail to detect either human or hamster LAMP-2. (B) FACS analysis of ldlD/hLAMP-2H cells and control ldlD cells stained with H4B4, a mAb to hLAMP-2 that cross-reacts with hamster LAMP-2. Surface expression of hLAMP-2 is detected only in transfected cells, whereas intracellular staining of native hamster LAMP-2 is apparent after permeabilization with saponin. (C) The sensitivity of the IIF assay for antibodies to hLAMP-2 assessed from doubling dilutions (1:50 to 1:800) of the standard positive control (Stand Co) compared with binding of monoclonal anti-hLAMP-2 antibody (H4B4; pos Co) and negative control serum (neg Co). IgG binding to ldlD/hLAMP-2H cells decreases progressively in titers >1:100 and becomes negative at 1:400, which is 10-fold higher than the standard assay dilution of 1:40.