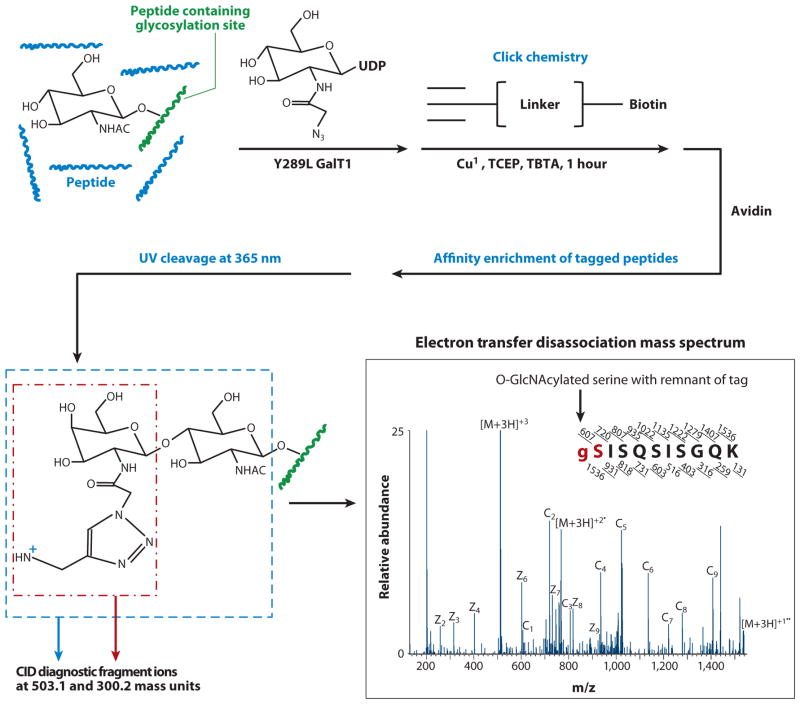
Figure 3.
Identification of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) sites is facilitated by photocleavable biotin tagging, combined with collision-assisted dissociation (CAD) and electron transfer dissociation (ETD) mass spectrometry. O-GlcNAc peptides are enriched by first labeling O-GlcNAc groups with N-azidoacetylgalactosamine (GalNAz) using a mutant galactosyltransferase (GalT1), followed by click chemistry addition of a photocleavable biotin tag. Tagged peptides are purified over an avidin column and subsequently are released from the beads by photochemical cleavage. CAD of tagged peptides generates diagnostic ions at mass/charge (m/z) 503.1 and 300.2. ETD enables peptide sequencing and O-GlcNAc site localization. An ETD spectrum of a sample peptide (SISQSISGQK) indicates that Ser1 is modified with a tagged GlcNAc-GalNAz moiety.