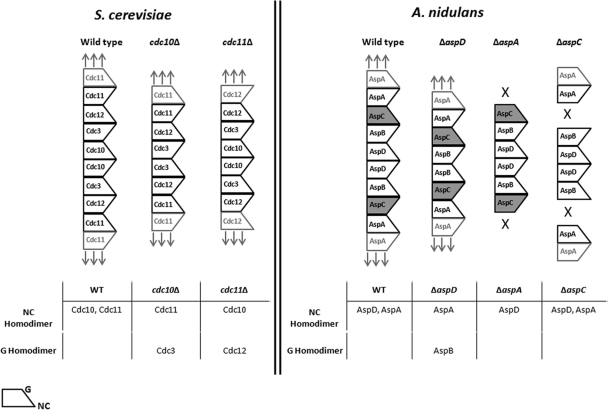
Fig 9.
Model of septin interactions in Aspergillus nidulans. (Left panel) Order of septin subunits in S. cerevisiae (adapted with permission from reference 6; additional data are from reference 43). (Right panel) Postulated order of septin subunits in A. nidulans. The wide end of septin subunit represents the NC interface; the narrow end represents the G interface. Boldface text denotes a single heteropolymer septin rod. The lighter text represents neighboring rods. Arrows indicate that septin polymer can be extended. X's indicate that septin polymer cannot be extended. Dark shading of AspC indicates that it differs from its S. cerevisiae ortholog Cdc12 because it is unable to form homopolymers via its G interface. See the text for further details.