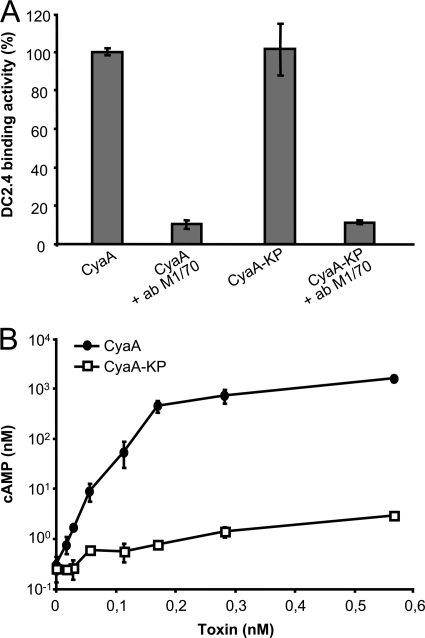
Fig 2.
Combination of the E570K and E581P substitutions selectively abolishes the AC domain translocation capacity of CyaA without affecting toxin binding to CD11b/CD18-expressing cells. (A) Mouse CD11b+ DC2.4 cells (2 × 106/ml) were incubated in the presence of 30 nM CyaA (AC+) in DMEM without FCS for 30 min on ice. After removal of the unbound toxin, the cell-associated adenylate cyclase enzyme activity was determined. To block the CD11b/CD18 receptor, cells were preincubated for 30 min on ice with 10 μg/ml of the CD11b-specific antibody M1/70 prior to addition of CyaA. DC2.4 binding activities are expressed as percentages of wild-type CyaA binding activity and are means ± standard deviations from two independent determinations performed in duplicate (n = 4). (B) cAMP levels in DC2.4 cells were determined upon 30 min of incubation of DC2.4 cells (3 × 105 per well) with the indicated toxin concentrations. Values are means ± standard deviations from two independent determinations performed in triplicate (n = 6).