Fig 7.
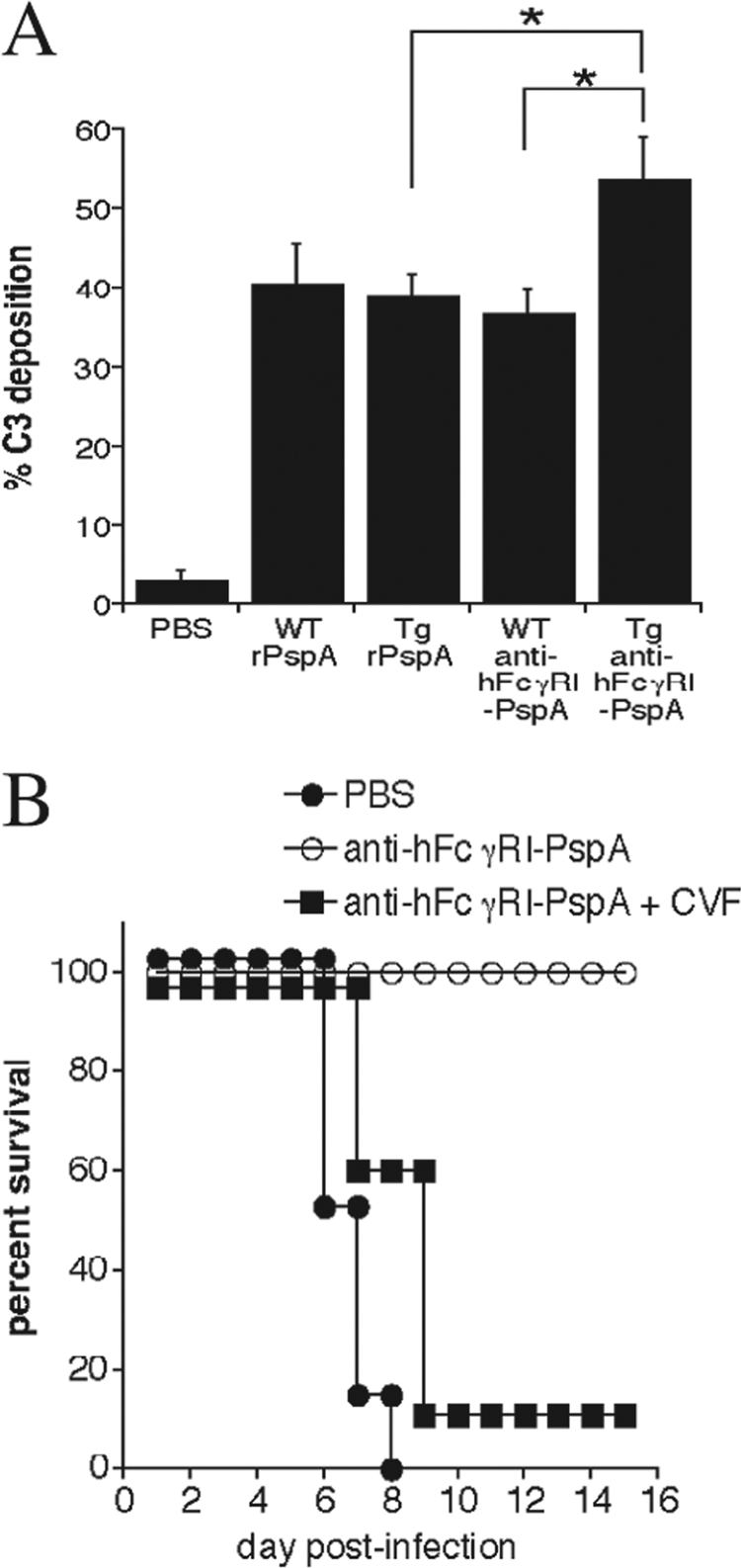
Targeting PspA to hFcγRI generates protection against S. pneumoniae, which is complement dependent. (A) Heat-inactivated sera from C57BL/6 WT and Tg mice, immunized with 25 μg of anti-hFcγRI-PspA, the rPspA equivalent to the anti-hFcγRI-PspA, or PBS, were incubated with 1 × 107 CFU of S. pneumoniae for 20 min at 4°C at a 1:2 dilution. Each bacterial sample was then incubated with 100 μl of mouse serum containing complement for 30 min. Deposition of C3 on S. pneumoniae was assessed by the addition of anti-C3 FITC monoclonal antibody followed by flow cytometry and analysis of the percentage of C3-positive bacteria (% C3) (*, P < 0.1). (B) Tg mice were immunized i.n. with PBS or 25 μg of anti-hFcγRI-PspA (day 0) followed by two boosts (days 14 and 28). One day prior to infection with S. pneumoniae (day 42), a group of hFcγRI-PspA-immunized mice received an i.p. injection of CVF (+CVF), which was repeated every 3 days thereafter. Survival of mice was monitored for at least 21 days. Five to 6 mice were used per group. The data are representative of a minimum of two independent experiments. For the anti-hFcγRI-PspA versus anti-hFcγRI-PspA +CVF group, P = 0.005.
