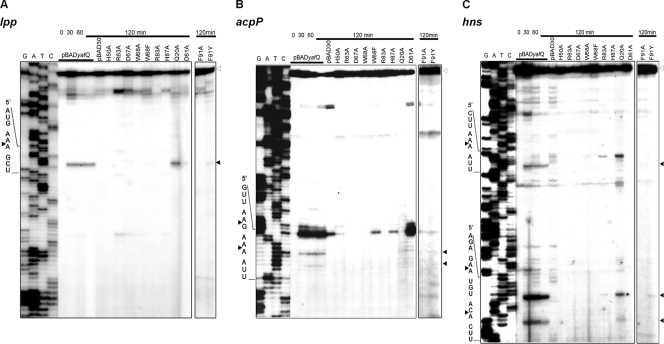
Fig 3.
Primer extension analysis of cellular transcripts after induction of YafQ mutant proteins in vivo. BW25113 strain containing plasmids pBADyafQ, pBAD30, or pBADyafQ with Gln20Ala, His50Ala, Asp61Ala, His63Ala, Asp67Ala, Trp68Ala, Trp68Phe, Arg83Ala, His87Ala, Phe91Ala, and Phe91Tyr substitutions were grown to mid-exponential phase, and the synthesis of YafQ was induced by adding 0.2% of arabinose as described in Materials and Methods. At selected time points, the total RNA was extracted and used for primer extension reactions with lpp-, acpP-, and hns-specific 5′-32P-labeled primers. The sequence ladder was obtained by dideoxy DNA sequencing reactions using the corresponding primers for primer extension. The cleavage sites of the YafQ toxin are indicated by full arrowheads, and the full-length RNAs are indicated by empty arrowheads.