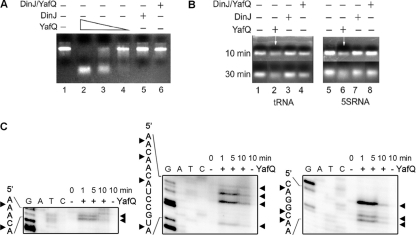
Fig 4.
Analysis of RNA cleavage by YafQ toxin in vitro. (A) In vitro-synthesized substrate (asr) mRNA (7.5 μg) was incubated for 30 min in 37°C in 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.0) with, respectively, 0.5, 0.25, and 0.1 μM YafQ(His)6 (lanes 2 to 4), 0.5 μM DinJ(His)6 (lane 5), and 0.5 μM DinJ-YafQ(His)6 protein complex (lane 6). (B) 5S rRNA or tRNA (0.16 μg) (lanes 1 and 5) was denatured at 70°C for 10 min and then incubated for 30 min in 37°C in 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.0) with 1 μM YafQ(His)6 (lanes 2 and 6), 1 μM DinJ(His)6 (lanes 3 and 7), 1 μM DinJ-YafQ(His)6 complex (lanes 4 and 8). The sample volume was 10 μl, and samples were analyzed in a 2% agarose gel, run for 10 or 30 min as indicated on the left (in panel B). (C) In vitro-synthesized substrate (hns) mRNA (0.2 μg) was incubated for 1, 5, or 10 min in 37°C in 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.0) with 2 μM YafQ(His)6 (“+” lanes) or without YafQ(His)6 (“−” lanes); the sample volume was 5 μl. After incubation, the samples were heat inactivated and used for primer extension reactions with hns-specific 5′-32P-labeled primers. The sequence ladder was obtained by dideoxy DNA sequencing reactions with corresponding primers used for primer extension. The cleavage sites of the YafQ toxin are indicated by full arrowheads.