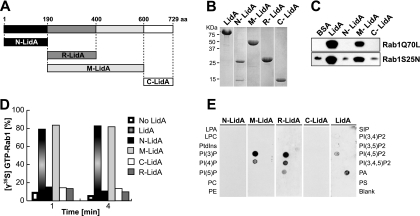
Fig 3.
LidA binds to Rab1 and phosphoinositides through its central coiled-coil region. (A) Schematic of LidA regions used for binding studies. (B) Purified full-length LidA and LidA variants. (C) Binding to Rab1 is mediated by the central region of LidA. Pulldown of constitutively active Rab1aQ70L or inactive Rab1aS25N by purified LidA or LidA variants (N-LidA, M-LidA, and C-LidA) immobilized on agarose beads was performed. Beads were incubated for 2 h at 4°C in the presence of a molar excess of either form of Rab1, and Rab1 bound to bead-immobilized proteins was detected by Western blotting. (D) The central region of LidA protects GTP-Rab1 from EDTA-mediated guanosine extraction. Rab1 was loaded with [γ35S]GTP and preincubated with full-length LidA or a truncated version of LidA for 1 min at room temperature. The release of radiolabeled guanosine nucleotides from Rab1 was stimulated by the addition of EDTA (20 mM final concentration). Loss of radioactive nucleotide was monitored by a filter-binding assay. Data are means ± standard deviations from three independent experiments. (E) The central region of LidA mediates binding to phosphoinositides. PIP Strip assays of full-length LidA or truncated versions of LidA (LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPC, lysophosphocholine; PtdIns, phosphatidylinositol; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; SIP, sphingosine-1-phosphate; P, phosphate; P2, biphosphate; P3, triphosphate; PA, phosphatidic acid; PS, phosphatidylserine). LidA binding was detected using anti-LidA antibody.