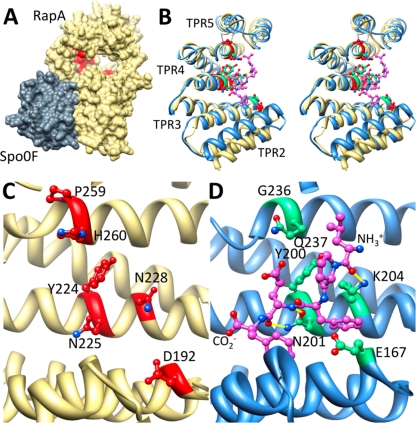
Fig 9.
Alanine scanning mutagenesis reveals the PhrA peptide binding pocket on RapA. (A) Shown is the structure of B. subtilis RapA (khaki), homology modeled on B. subtilis RapH in complex with Spo0F (gray). RapA alanine mutants unable to bind and respond to PhrA are in red, demonstrating that the PhrA peptide binding site is distal from the Spo0F binding site and on the concave face of the TPR domain. (B, C, and D Stereo view overlay (B) or side-by-side view (C and D) of TPR2-5 of RapA (khaki) with the equivalent of PlcR (blue); compare the position of alanine mutants unable to bind PhrA peptides (red) to the position of the PapR peptide ligand (magenta). Sites on PlcR that correspond to the RapA alanine mutants are in green. Hydrogen bonds between the peptide and the displayed PlcR residues are in yellow. Amino- and carboxy-terminal ends of the PapR peptide are as labeled.