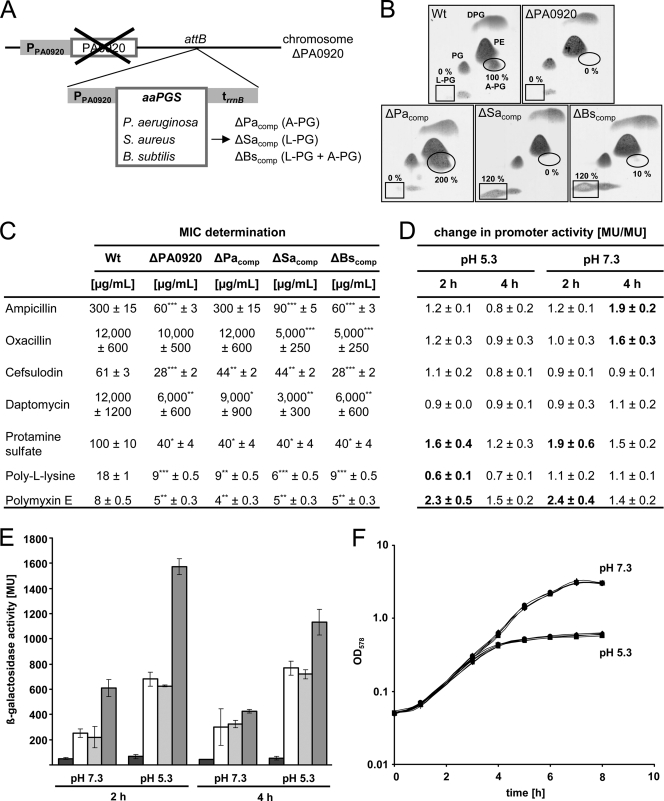
Fig 1.
Construction and analysis of complemented P. aeruginosa mutant strains. (A) Chimeric P. aeruginosa mutant strains were constructed by the chromosomal complementation of the ΔPA0920 deletion mutant with orthologous aaPGS genes from S. aureus (ΔSacomp) and B. subtilis (ΔBscomp) strains at the attB locus, and analogously a homologous complemented strain (ΔPacomp strain) was generated. Resulting strains are devoid of any resistance marker, and the related specificity of the individual aaPGS gene for the synthesis of A-PG and/or L-PG is indicated. PPA0920, native promoter region of ORF PA0920 (187 bp); trrnB, rrnB terminator sequence (158 bp); attB, attachment site B locus. (B) Lipid composition of P. aeruginosa mutant strains. Cells were cultivated in AB medium (pH 5.3) and harvested, and polar lipids were extracted and separated by two-dimensional TLC. Lipids were visualized by molybdatophosphoric acid staining. The specific positions of A-PG and L-PG are indicated by an ellipse and a rectangle, respectively. Relative amounts of A-PG and L-PG were quantified using Gelscan 6.0 software. The A-PG level of the wild-type strain was defined as 100%, and all other values were related to this. (C) MICs were determined by treating the strains with gradually varying inhibitor concentrations in AB medium, pH 5.3. Significance analysis revealed P values of ≤0.1 (*), P values of ≤0.05 (**), and P values of ≤0.01 (***). (D) The promoter activity of the P. aeruginosa A-PGS gene was analyzed using a transcriptional PPA0920-lacZ fusion. Cells were grown in AB medium, pH 5.3 and 7.3, in the presence of subinhibitory concentrations of antimicrobials, and β-galactosidase activity was determined after 2 and 4 h of cultivation, respectively. To evaluate the individual effect of each compound, observed MU were expressed as an induction ratio (the ratio of Miller units in the presence and absence of the antimicrobial compound). A ratio of >1 indicates transcriptional activation due to the presence of a specific compound. (E) Selected promoter activities (from panel D) are indicated to demonstrate the influence of antibiotics, pH, and the cultivation time. MU values for untreated cultures are indicated with white bars and for the promoterless control strain KS11 with black bars. Promoter activities in the presence of daptomycin and polymyxin E are indicated in light gray and dark gray, respectively. (F) Growth curves for P. aeruginosa variants were determined by measuring the turbidity at 578 nm in AB medium, pH 5.3 and pH 7.3. Rhombus, wild type; quadrat, ΔPA0920 strain; triangle, ΔPacomp strain; dot, ΔSacomp strain; plus, ΔBscomp strain. For experimental details, see Materials and Methods. A-PG, alanyl-phosphatidylglycerol; L-PG, lysyl-phosphatidylglycerol; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PG, phosphatidylglycerol, DPG, diphosphatidylglycerol.