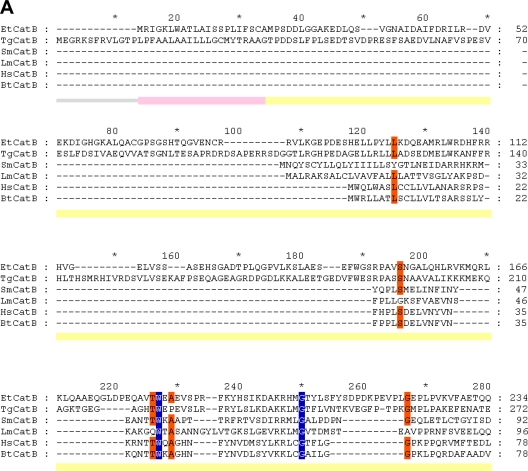
Fig 1.
Protein sequence alignment of the prepro-EtCatB with cathepsin B enzymes from different organisms. (A) Preproregions. (B) Mature regions. EtCatB, E. tenella cathepsin B; TgCatB, T. gondii cathepsin B (31); SmCatB, S. mansoni cathepsin B (8); LmCatB, L. major cathepsin B (36); HsCatB, Homo sapiens liver cathepsin B (11); BtCatB, B. taurus cathepsin B (4). GenBank accession numbers are as follows: TgCatB, AY071839; SmCatB, AJ312106; LmCatB, U43705; HsCatB, M14221; BtCatB, L06075. Information on EtCatB is available on the GeneDB website (http://www.genedb.org/gene/ETH_00003570.1?actionName=%2FQuickSearchQuery). Highly conserved and conserved residues are highlighted by blue and orange backgrounds, respectively. (A) The predicted signal peptide (prepeptide) of EtCatB is marked by a rose bar, and the prodomain is marked by a yellow bar. (B) Start of the mature EtCatB is indicated by a vertical arrow. Residues of the S2 pocket are indicated by a green background. The K496E (K261E, mature enzyme numbering) exchange between EtCatB and BtCatB is marked with blue circles. The catalytic triad (C, H, and N) is indicated by magenta asterisks. The potential N-glycosylation site of EtCatB is marked with a gray circle. Cysteines of disulfide bridges are highlighted by yellow backgrounds. The six disulfide bridges of EtCatB are marked by black lines with different heads. The additional disulfide bridge of BtCatB is marked by a cyan line. Secondary structure elements are indicated schematically beneath the alignment. The seven β-sheets are indicated by green block arrows, and the four α-helices are indicated by red banners.