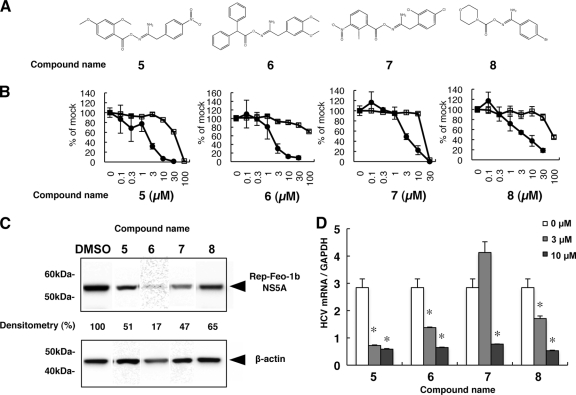
Fig 5.
Effects of derivatives of compound 1 on HCV replication. (A) Chemical structures of screening hits of compound 1 derivatives. (B) Huh7/Rep-Feo cells were treated with various concentrations of each compound for 48 h. Luciferase activity for HCV RNA replication is shown as a percentage of the DMSO-treated control luciferase activity (solid circles). Cell viability is also shown as a percentage of control viability (open squares). Each point represents the mean of triplicate data points, with standard deviations represented as error bars. (C) HCV NS5A protein expression levels in Huh7/Rep-Feo cells after treatment with the hit compounds. Huh7/Rep-Feo cells were treated with DMSO and derivative compounds at 5 μM for 48 h, and Western blotting was performed using anti-HCV NS5A and anti-β-actin antibodies. Densitometry of the NS5A protein was performed, and the results are indicated as percentages of the DMSO-treated control. The assay was repeated three times, and a representative result is shown. (D) Huh7.5.1 cells were transfected with HCV-JFH1 RNA and cultured in the presence of the indicated compounds at a concentration of 3 μM or 10 μM. At 72 h after transfection, total cellular RNA was extracted, followed by real-time RT-PCR. The bars indicate means and SD. The asterisks indicate P values of less than 0.01. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.