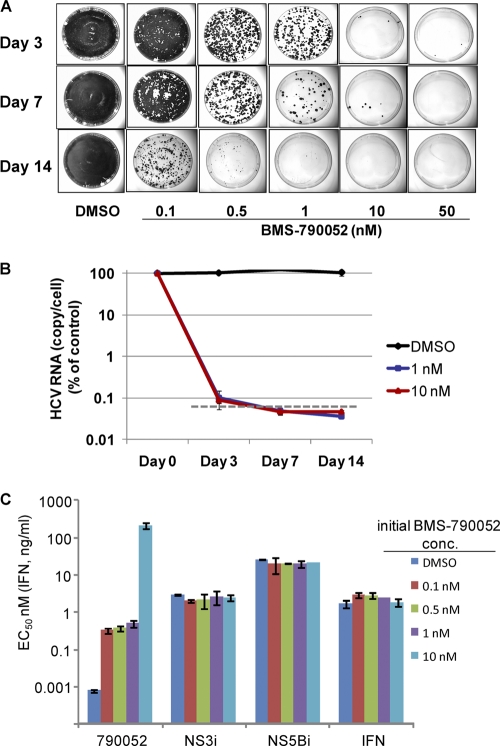
Fig 1.
(A) Replicon elimination and colony formation assays with Con1 replicon cells. Colonies formed from replicon-retaining cells following treatment with BMS-790052 for the indicated durations and concentrations were stained and photographed. (B) Decline in replicon RNA over time in Con1 replicon cells treated with BMS-790052 or DMSO. The level of replicon RNA in cells treated with BMS-790052 or DMSO was measured by quantitative RT-PCR and is plotted on a log scale as the percentage relative to that in untreated control cells. Data points are the means and standard deviations from three replicate experiments. The dashed line represents the lower level of detection as determined from assays performed with non-replicon-containing Huh7 cells. (C) Inhibitor sensitivities of replicon cells recovered after 7 days of treatment with BMS-790052. Replicon cells recovered from a parallel set of tissue culture dishes to those described in Fig. 1A were used to determine the inhibitory activity of the indicated HCV inhibitors. EC50s are plotted as the means ± standard deviations from two independent assays. The initial BMS-790052 concentration (conc.) is the concentration at which the cells were treated for 7 days prior to removing inhibitor and adding G418. NS3i, BMS-650032; NS5Bi, BMS-791325; IFN, pegIFN-α2a.