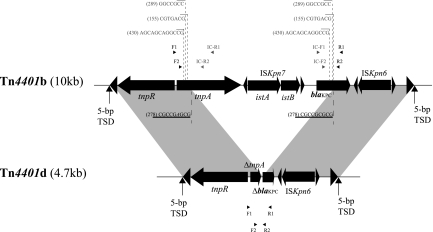
Fig 1.
Structure of truncated Tn4401 variant Tn4401d. Gray shading denotes regions of homology shared by Tn4401b and Tn4401d. Open reading frames (ORFs) are portrayed as large black arrows. Excision sites found in BK32529 are indicated by dotted lines beneath Tn4401b, with characteristic direct repeat (DR) sequences underlined. Imperfectly homologous sequences (with mismatches) within the two DRs are shown in italics. Numbers within parentheses denote the nested-PCR product sizes listed in Table 2. Additional potential excision sites determined by nested PCR are indicated by dotted lines above Tn4401b, with the corresponding direct repeat sequences shown in gray. Small black arrowheads represent the locations of primers used for nested PCR; small gray arrowheads indicate the locations of primers used for outward-directed nested PCR. Primers used for nested PCR were as follows: F1 (AATGCCCCATGTTTCTACGA), R1 (GGTCGTGTTTCCCTTTAGCC), F2 (TCACCAAGCATGAACGCTAC), and R2 (GCAGAGCCCAGTGTCAGTTT). Primers used for outward-directed nested PCR were as follows: IC-F1 (ATCGCCGTCTAGTTCTGCTG), IC-R1 (CAGCAGGTAGAGTTGGGTCTG), IC-F2 (CAGCTCATTCAAGGGCTTTC), and IC-R2 (CGTCGAGTTTAGGCAGCAGT). TSD, target site duplication.