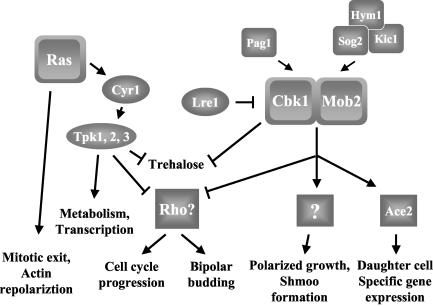
FIG. 9.
Model for the roles of Ras and Mob2 in S. cerevisiae. Ras proteins have PKA-independent functions in mitotic exit and actin repolarization and PKA-dependent functions affecting metabolism, transcription, and cell growth. Cbk1, together with Mob2, regulates the Ace2 transcription factor, effecting daughter cell-specific gene expression. Cbk1 and Mob2 have additional Ace2-independent functions in regulating apical growth and mating projection formation. Hym1 interacts with Kic1 and Sog2, and this complex along with Pag1 interacts with Cbk1 to promote its localization and function. Data presented in this report demonstrate that the Ras/PKA and Cbk1/Mob2 pathways play parallel roles in cell growth and bud site selection, likely through regulation of Rho1 (see Discussion for details). Cbk1 and the Ras/PKA pathway independently repress cellular trehalose levels through a different mechanism.