Fig 1.
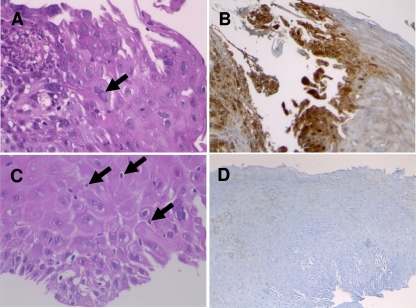
Histopathological aspect of herpetic (A and B) and nonherpetic (C and D) esophagitis biopsy specimens. (A) HSV esophagitis: typical multinucleated epithelial cells with ground-glass nuclei and margination of the chromatin (black arrow). HPS stain; magnification ×400. (B) Immunohistochemical detection of HSV glycoproteins (in brown) in epithelial cells. Magnification, ×100. (C) Non-HSV esophagitis: neither multinucleated nor ground-glass nuclei; intraepithelial exocytosis of lymphocytes (black arrows). HPS; magnification, ×400. (D) Negative immunohistochemical detection of HSV antigens. Magnification, ×100.