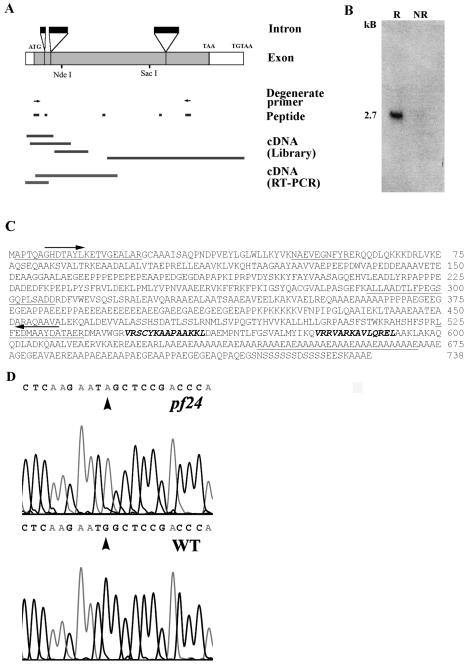
FIG. 4.
(A) Strategy for cloning RSP2 starting with peptide sequences from band-purified RSP2 (see Materials and Methods). PCR, using the degenerate oligonucleotide primers (arrows) derived from two peptides, resulted in a probe for screening cDNA and genomic libraries. Additional RT-PCR was carried out to recover entire cDNA. The coding sequence (gray boxes), untranslated regions (open boxes), and introns (black boxes) were deduced by comparing complete genomic, cDNA, and peptide sequences. (B) Northern blot analysis, with the RSP2 RT-PCR probe, revealed a 2.7-kb message that became greatly amplified in cells 45 min following deflagellation (R, RNA from flagellar regenerating cells; NR, RNA from control, nonregenerating cells). (C) Predicted amino acid sequences of RSP2 (accession no. AY373262). Sequences obtained by peptide microsequencing are underlined. Arrows indicate the peptide sequences used for designing degenerate oligonucleotide primers for successful RT-PCR, and boldface italic indicates amphipathic helical domains predicted to bind calmodulin (Fig. 5 and 6). (D) Comparison of wild-type and pf24 RSP2 genomic sequences, revealing that the pf24 mutation results from a single base pair replacement and conversion of the initial ATG to ATA. WT, wild type.