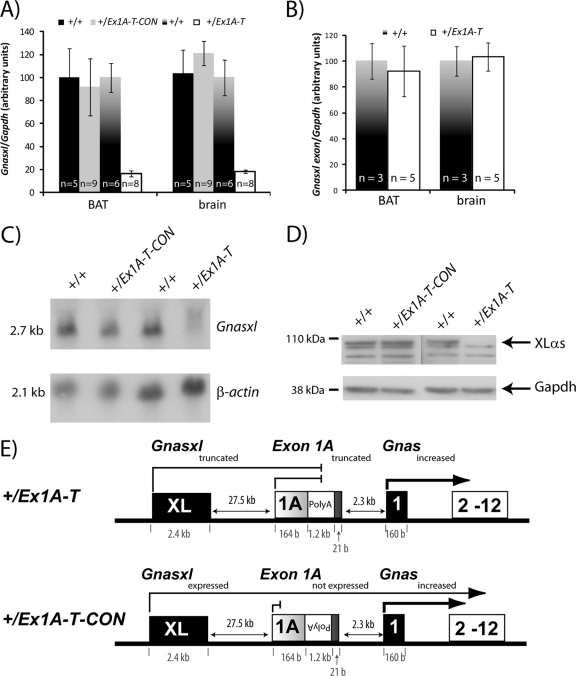
Fig 4.
Truncation of Gnasxl. (A) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of Gnasxl transcript in newborn tissues. Primers were designed at the end of the Gnas XL exon and at the start of Gnas exon 2. Expression was normalized to Gapdh. Error bars indicate the standard errors of the means; P < 0.005. (B) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of Gnasxl transcript in newborn tissues. Primers were designed at the start and end of the Gnas XL exon. Expression was normalized to Gapdh. Error bars indicate the standard errors of the means. (C) Northern blot assay of Gnasxl and a β-actin loading control in E15.5 whole embryos. Results shown are representative of 3 to 5 samples per genotype. (D) Western blot assay of XLαs and a GAPDH loading control in E15.5 whole embryos. Samples shown are representative of at least two samples analyzed per genotype. (E) Schematic diagram summarizing the outcomes of the poly(A) cassette insertion in the +/Ex1A-T and +/Ex1A-T-CON mutations on Gnas cluster transcripts on the paternal allele.