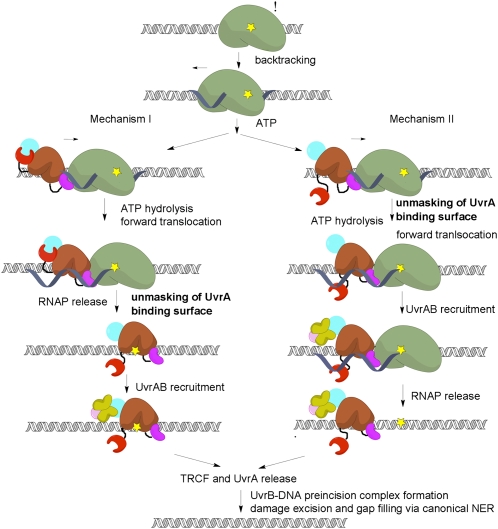
Fig. 5.
TCR mechanisms. RNAP (green) stalls at DNA lesions (yellow) in the template strand and backtracks, recruiting TRCF, which promotes forward translocation of RNAP using ATP hydrolysis by the translocase module (brown) and, eventually, TEC dissociation. Next, the UvrAB complex is recruited by virtue of the unmasking of the UvrA-binding surface in D2 by motion of D7. The timing of UvrA recruitment differs in these two models, but our data argue for a sequential model (mechanism I). The pathway continues with formation of an UvrB–DNA preincision complex, subsequent DNA incisions, and gap filling (36).