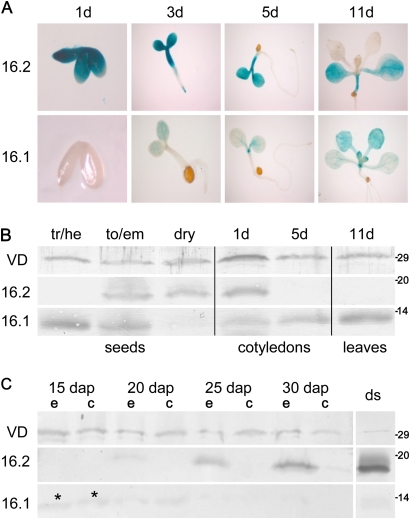
Fig. 3.
OEP16.1 and OEP16.2 expression during seed development and germination. (A) Histochemical detection of GUS activity directed by the At-OEP16.1 and At-OEP16.2 promoter in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. GUS expression was monitored after germination for 1, 3, 5, and 11 d. For the 1-day-old tissue (1d) the seed coat was removed manually. Pictures show representative results for at least three different transgenic lines. (B) Immunoblot analysis of At-OEP16.1 and At-OEP16.2 in protein extracts from developing seeds (tr/he, transition/heart stage; to/em, torpedo/embryo stage), dry seeds, cotyledons (1–5 d old), and leaves (11 d old) of seedlings. For seeds 10 μg, and for seedlings 20 μg of protein were loaded in each lane. (C) Immunoblot of Ps-OEP16.2 and Ps-OEP16.1 in protein extracts (4 μg each) from developing and dry (ds) pea seeds. Seed stages are given in days after pollination (dap). During development seeds were separated into embryo (e) and seed coat (c) tissue, the latter containing endosperm layers. Asterisks indicate weak OEP16.1 signals in early embryo and seed coat (15 dap). (B and C) Antiserum against the marker protein VDAC (outer membrane of mitochondria) was used as loading control. Numbers indicate the molecular mass of proteins in kDa.